40 diagram of sperm
Sperm diagram class 8|how to draw human sperm easilyHi friends, In this video we will learn how to draw diagram of human sperm (this diagram is ba... Q.2. Draw a labelled diagram of the reproductive system in a human female. Ans. Diagrammatic sectional view of the female reproductive system Q.3. Draw a diagram of the microscopic structure of human sperm. Label the following parts in it and write their functions. (i) Acrosome (ii) Nucleus (iii) Middle piece OR Draw a diagram of a human sperm.
Draw a labelled diagram of sperm. Solution ... Draw labelled diagrams to show the fertilisation of an ovum (or egg) by a sperm to form a zygote. Science | P S Verma Biology (2020, 2021) All. Q3. Draw a well labelled diagram of phloem. Biology | NCERT Standard XI. Q4.

Diagram of sperm
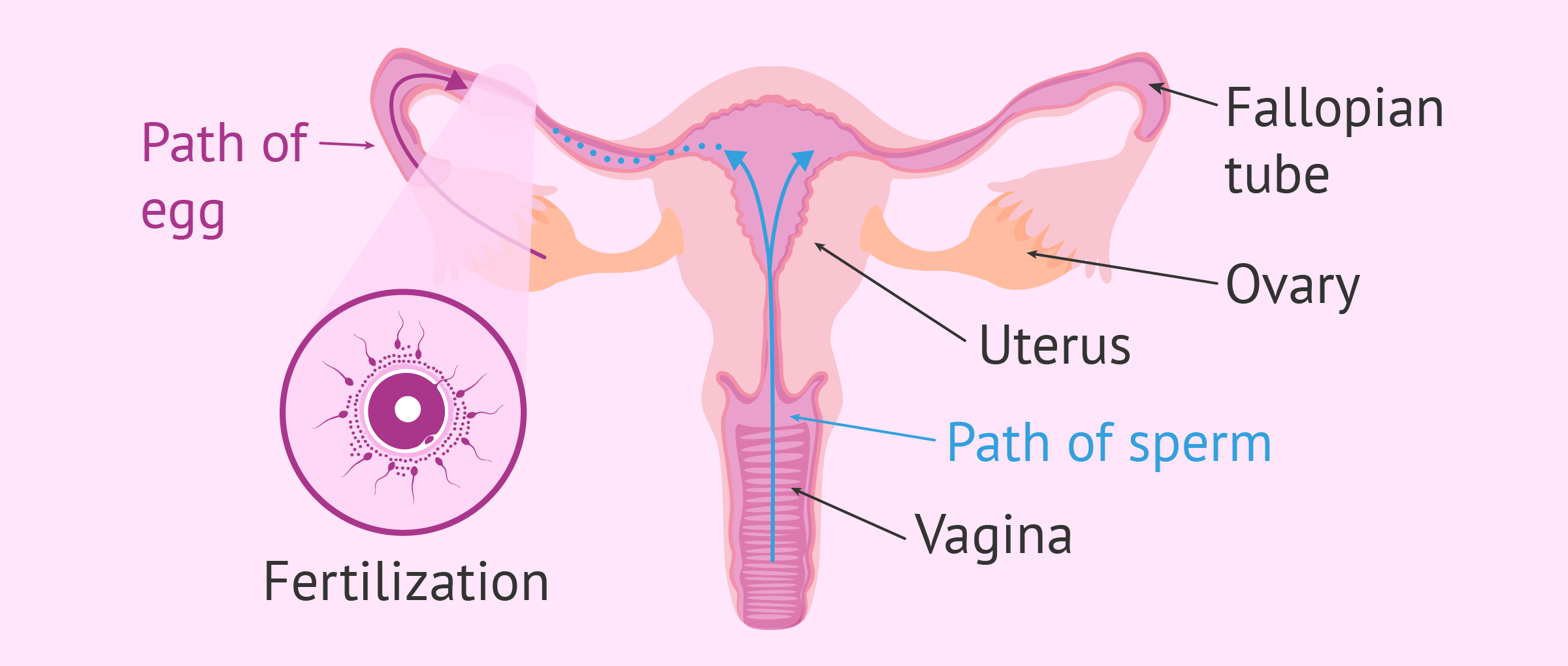
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. ... Aug 16, 2021 · Cancer isn’t usually top of mind for young women, but this type -- caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) -- is a serious threat. Each year, more than 11,000 women get the disease. human reproductive system, organ system by which humans reproduce and bear live offspring. Provided all organs are present, normally constructed, and functioning properly, the essential features of human reproduction are (1) liberation of an ovum, or egg, at a specific time in the reproductive cycle, (2) internal fertilization of the ovum by spermatozoa, or sperm cells, (3) transport of the ...
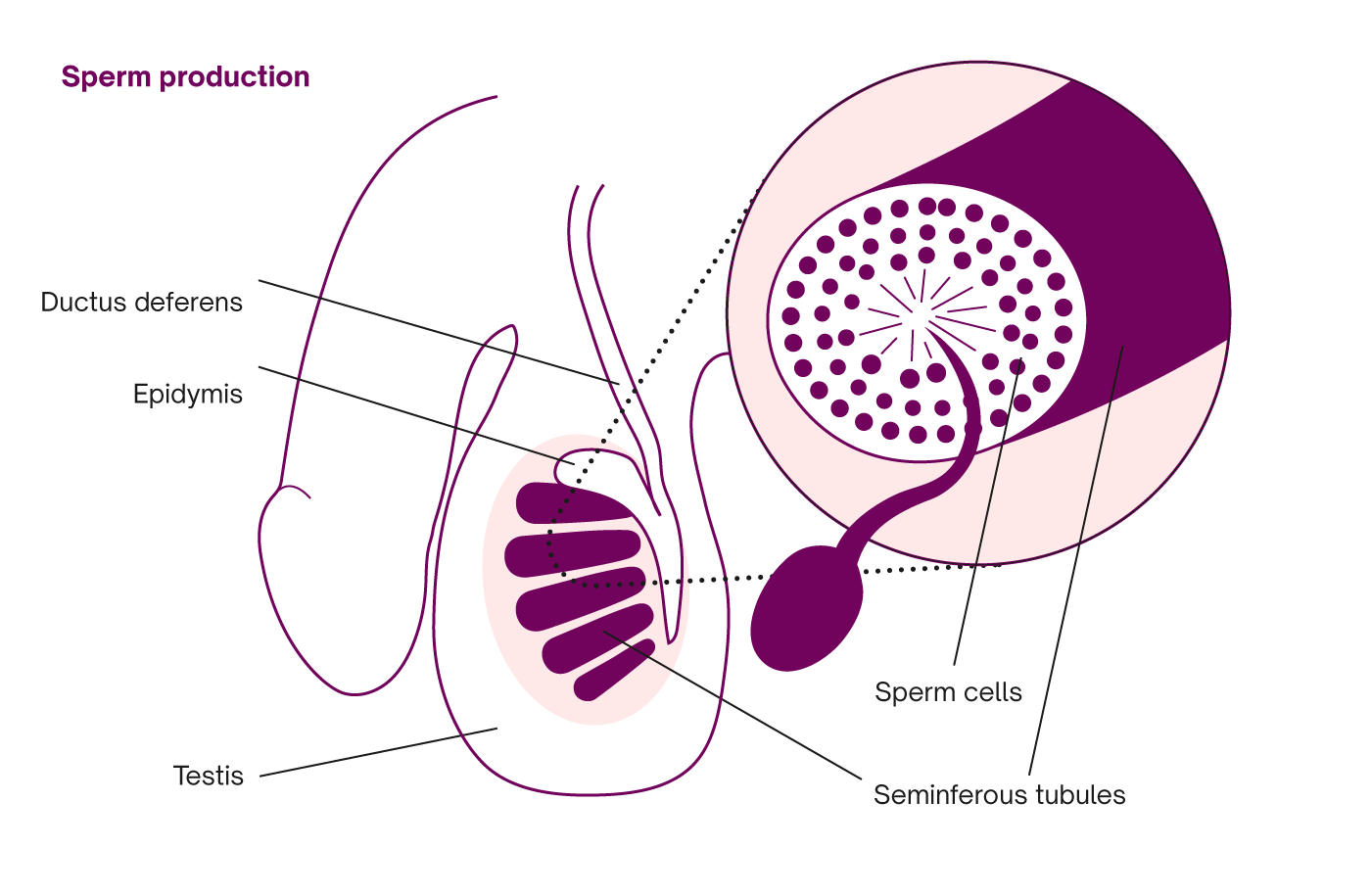
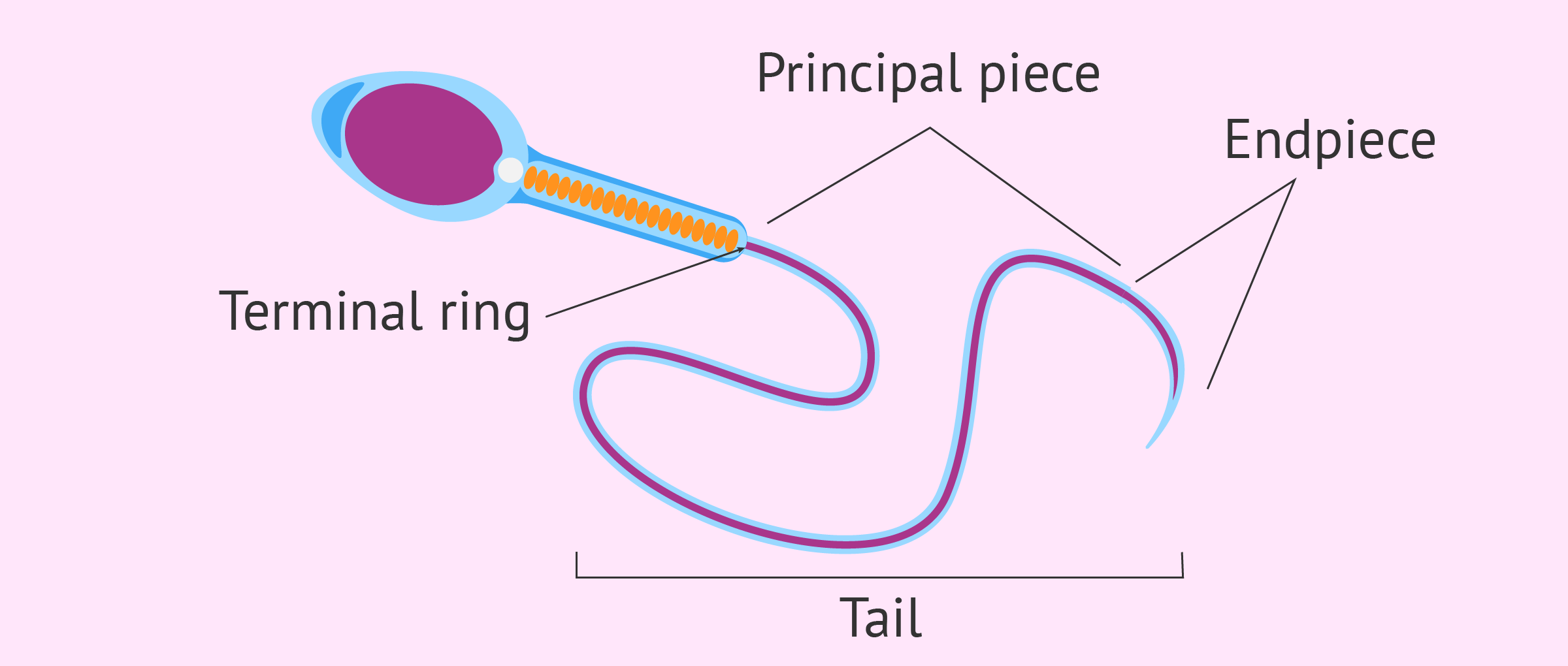
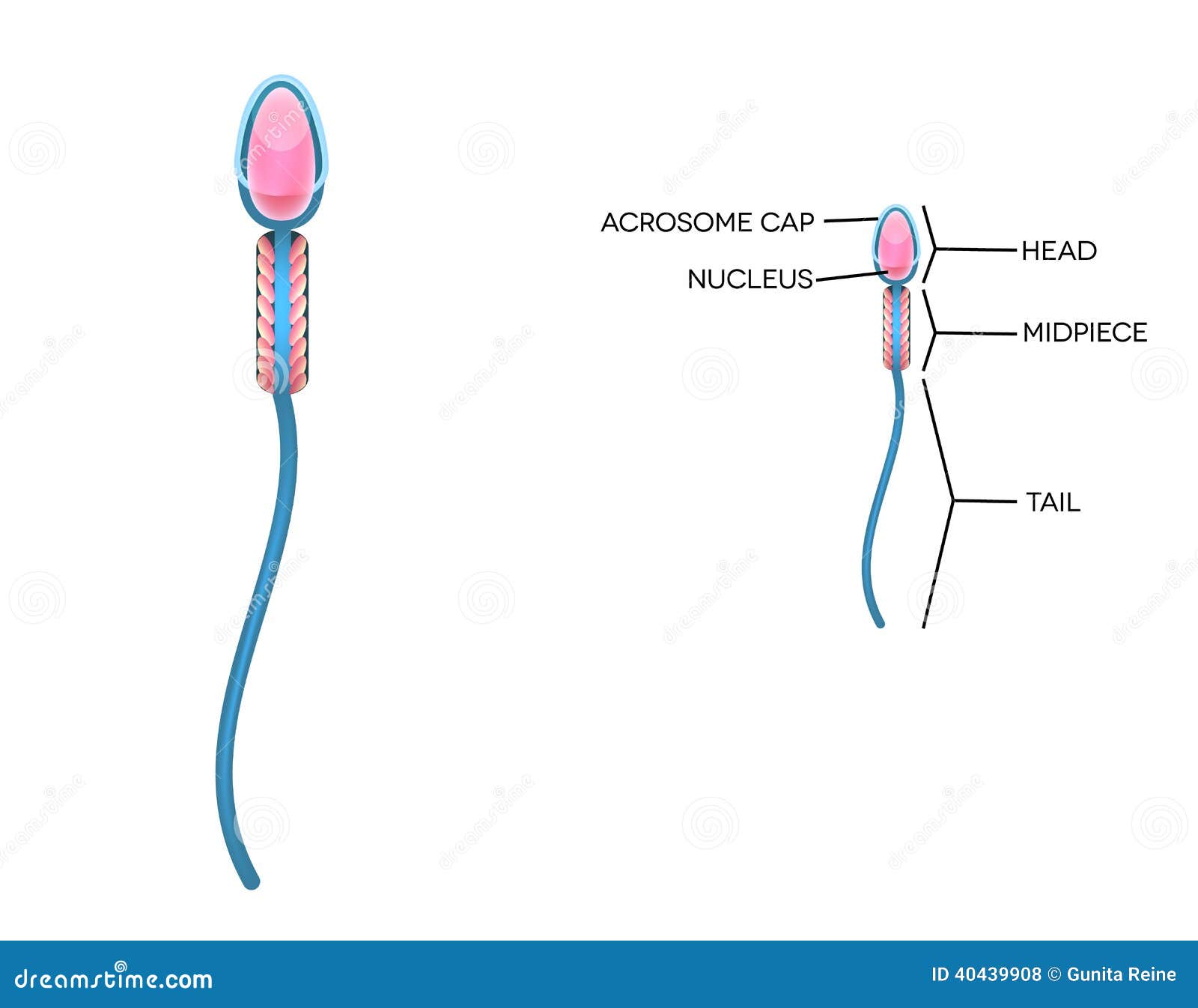
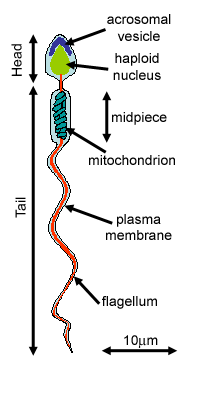
Diagram of sperm. This is The Garbage Truck Song by Blippi. Your child will love this Blippi video of garbage trucks for kids. For more Blippi videos and garbage truck videos ... May 29, 2018 · The rete testis helps to mix sperm cells around in the fluid secreted by Sertoli cells. The body reabsorbs this fluid as sperm cells travel from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis. Human sperm is a microscopic structure whose shape is like a tadpole. It has flagella which makes it motile. Its diameter is 2 – 5 μ m, and its length is 60 μ m. It is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It has no nutritive material. It lacks most of the cell organelles like ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. Structure of Sperm. The Head contains acrosome apically, which contains enzymes that facilitate the entry of sperm into the ovum. It is followed by an elongated nucleus (haploid) The tail is a flagellum that protrudes out of the cell body and is responsible for the vigorous motility of sperms. The tail helps sperms in swimming so that they can ...
The acrosome is an organelle that develops over the anterior half of the head in the spermatozoa (sperm cells) of many animals including humans. It is a cap-like structure derived from the Golgi apparatus.In Eutherian mammals the acrosome contains degradative enzymes (including hyaluronidase and acrosin). These enzymes break down the outer membrane of the ovum, called the zona pellucida ... The sperm cells are the haploid gametes which are produced in the male. There are different parts of the sperm cell. (a) Acrosome: This structure contains enzymes used for penetrating the female egg. (b) Nucleus: There is the genetic material which is a haploid genome because it contains only one copy of each chromosome. Popular Questions of Class 12 Biology. Q:-Why is reproduction essential for organisms?Answer; Q:-What is spermatogenesis?Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis. Q:-With a neat diagram explain the 7-celled, 8-nucleate nature of the female gametophyte.Q:-Write a short note on(a) Adaptations of desert plants and animals Mendel deduced that sex cells — sperm and eggs — contain only one parental gene of each pair. The half-sets of genes contributed by sperm and egg restore a whole set of genes in the offspring. Mendel found that different gene combinations from the parents …
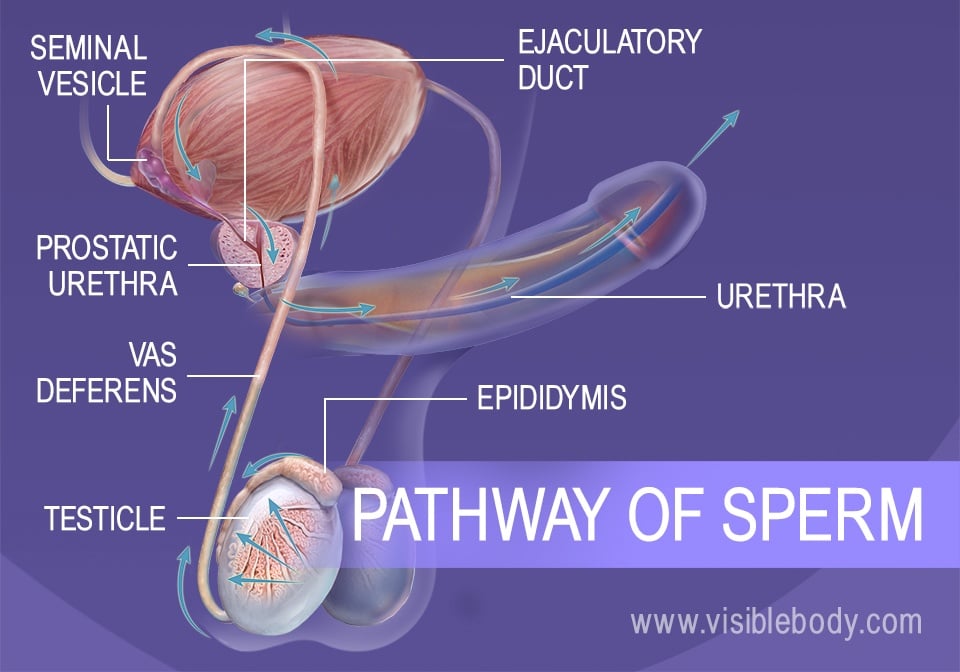
Stomach, saclike expansion of the digestive system, between the esophagus and the small intestine; it is located in the anterior portion of the abdominal cavity in most vertebrates. The stomach serves as a temporary receptacle for the storage and mechanical distribution of food before it … The testes are the primary reproductive organs and generate sperm cells through a process called spermatogenesis. The glands of the male reproductive system produce sperm and seminal fluid. The prostate gland, the seminal vesicles, and the bulbourethral glands contribute seminal fluid to semen, which carries and protects the sperm. Structure of Human Sperm. Human Sperm is the small tadpole-like motile, functional, haploid male gamete produced in the testes by the process called spermatogenesis. The human sperm is microscopic and measures about 40-45 µm in length. Structurally, the sperm is divisible into the head, neck, middle piece and tail. The testes are where sperm are manufactured in the scrotum. The epididymis is a tortuously coiled structure topping the testis, and it receives immature sperm from the testis and stores it for several days. When ejaculation occurs, sperm is forcefully expelled from the tail of the epididymis into the deferent duct. Sperm then travels through ...
Structure of human sperm. Function of Acrosome-It releases various chemicals like hyaluronidase and acrosin which helps sperm in fusing with egg cell. Function of Nucleus-It stores the genetic information. It carries 23 chromosomes, out of which one is sex chromosome (either X or Y). Thus, it is responsible for determining the sex of the ...
Jan 23, 2018 · The penis is the main part of external male genitalia, which has both sexual and bodily functions. It is able to ejaculate semen (containing sperm) during sex and to relieve the body of urine.
human reproductive system, organ system by which humans reproduce and bear live offspring. Provided all organs are present, normally constructed, and functioning properly, the essential features of human reproduction are (1) liberation of an ovum, or egg, at a specific time in the reproductive cycle, (2) internal fertilization of the ovum by spermatozoa, or sperm cells, (3) transport of the ...
Aug 16, 2021 · Cancer isn’t usually top of mind for young women, but this type -- caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) -- is a serious threat. Each year, more than 11,000 women get the disease.
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. ...
Explain The Structure Of Human Sperm With Diagram Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Human Sperm And Egg Fusion Diagram With All Fertilization Process And Stages Step By Step Including Contact Acrosomal Cortical Reaction Growth Fusion Of Plasma Membrane Entry Of Sperm Nucleus Royalty Free Cliparts

Draw A Diagram Of The Microscopic Structure Of Human Sperm Label The Following Parts In It And Write Their Functions

Sperm Development Espermatozoide Diagram Of A Human Sperm Cell Stock Vector Vector And Low Budget Royalty Free Image Pic Esy 058915520 Agefotostock
Complete Diagram Of A Human Spermatozoa Clip Art At Clker Com Vector Clip Art Online Royalty Free Public Domain
























Comments
Post a Comment