43 extracellular matrix diagram
The laminins are heterotrimeric proteins of the extracellular matrix that are composed of α-, β- and γ-subunits. Currently, in mouse and human, genes encoding five α-, three β- and three γ-subunits have been identified ().When known splice variants are included, these subunits assemble into at least 16 different laminin heterotrimers (Aumailley et al., 2005) (). Modify. 2021-11-03. The extracellular matrix is a component of all mammalian tissues, a network consisting largely of the fibrous proteins collagen, elastin and associated-microfibrils, fibronectin and laminins embedded in a viscoelastic gel of anionic proteoglycan polymers. It performs many functions in addition to its structural role; as a ...
And it is true that the extracellular matrix, the collagen fibers and other things that we find there help attach the cells and structure the cells into tissues. They also help inform the cell, let the cell know when to grow, when to divide, even potentially when to die or when to produce different types of molecules.

Extracellular matrix diagram
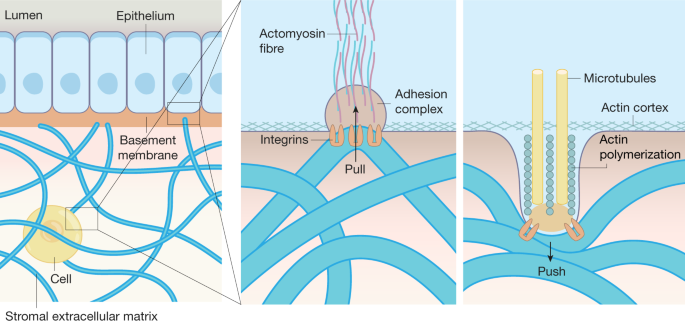
The Extracellular Matrix. The extracellular matrix (ECM) is made up of 3 main elements: Aggrecans (10%) Water (75%) Collagen fibres and other constituents (15%) Aggrecans are proteoglycans which is a molecule made up of carbohydrates (repeating disaccharide units known as glycosaminoglycans or GAGs) attached to a protein core. Cytoskeletal fences (corrals) and binding to the extracellular matrix. Some proteins embedded in the bilipid layer interact with the extracellular matrix outside the cell, cytoskeleton filaments inside the cell, and septin ring-like structures. These interactions have a strong influence on shape and structure, as well as on compartmentalization The extracellular matrix (ECM) is the non-cellular component present within all tissues and organs, and. provides not only essential physi cal scaffolding for the cellular constituents but also ...
Extracellular matrix diagram. Extracellular matrix labeled infographic vector illustration scheme.. Illustration about carbohydrates, head, graphic, environment, diagram, core, extracellular, cell - 125798054 Aug 25, 2021 · The extracellular matrix is a network of fibrous proteins and proteoglycans that fills the space between the cells within your tissues. The components of the extracellular matrix are usually the ... This problem has been solved! 1.1. Draw a diagram and briefly describe the extracellular matrix. 1.2. Sketch simple diagrams which explain about the different ways plant cells communicate with adjacent cells. 1.3. Summarize the roles of tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and plasmodesmata. The extracellular matrix (ECM) is critical for all aspects of vascular biology. In concert with supporting cells, endothelial cells (ECs) assemble a laminin-rich basement membrane matrix that provides structural and organizational stability. During the onset of angiogenesis, this basement membrane matrix is degraded by proteinases, among which ...
Components and structure of the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix of the human body includes: Interstitial matrix : is the intercellular space, the space that remains between some cells and others within a tissue. It is occupied by a kind of aqueous gel of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins , together with other molecules dispersed in it, such as electrolytes, enzymes and ... Extracellular matrix is the extracellular, complex mixture of various biomolecules and fibers secreted by cells in the tissues of multicellular organisms. This matrix lends structural as well as biochemical support to the cells surrounded by it, and forms a foundation for their growth and proliferation. BiologyWise provides an in-depth study of the components, structure, and function of ... Granzyme B (GrB) is a serine protease most commonly found in the granules of natural killer cells (NK cells) and cytotoxic T cells.It is secreted by these cells along with the pore forming protein perforin to mediate apoptosis in target cells. Aug 05, 2021 · Here the authors combine human brain extracellular matrix and culture in a microfluidic device to promote structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids. ... a Schematic diagram of ...
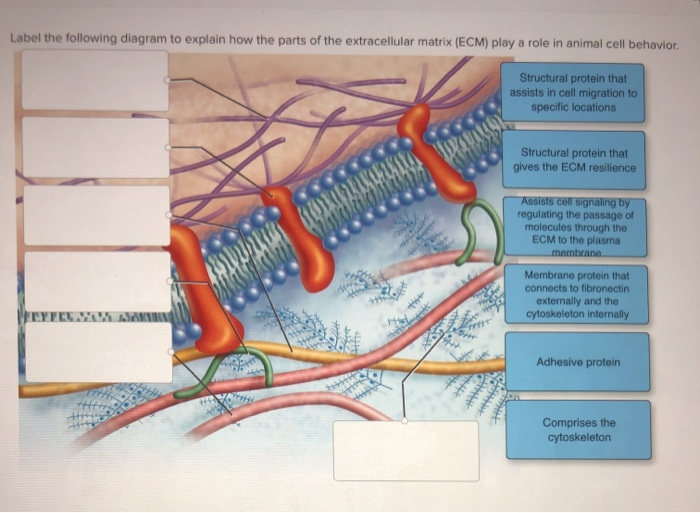
The extracellular matrix (ECM) contains fibrous proteins, proteoglycans and hyaluronon. Fibrous proteins and hyaluronan primarily provide structure support. Proteoglycans appear to form a gel that varies in pore size and regulates the diffusion of molecules. View Extracellular-Matrix-With-Diagram-_-Cell-Biology.pdf from MEDTECH 123 at University of Baguio. Extracellular Matrix (With Diagram) | Cell Biology Subject-Matter of Extracellular Matrix: Animal Extracellular matrix (ECM) presents in the muscle niche and is composed of proteins, polysaccharides [ 3 ], and RNA [ 4] etc., which plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating the development of skeletal muscle [ 5 ]. The ECM of skeletal muscle tissue contains three layers. The innermost structure is called the basal ... The extracellular matrix (ECM) is the non-cellular component present within all tissues and organs, and provides not only essential physical scaffolding for the cellular constituents but also initiates crucial biochemical and biomechanical cues that are required for tissue morphogenesis, differentiation and homeostasis.
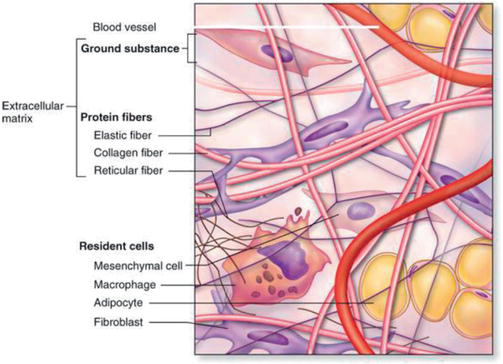
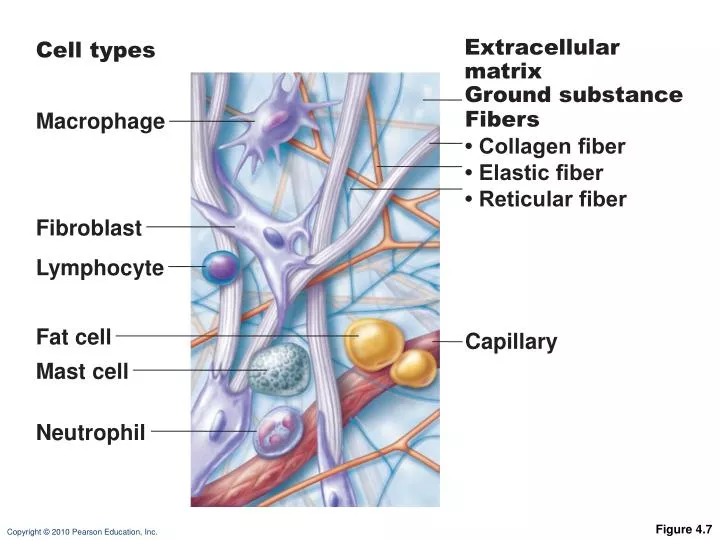
The 'ground substance' of extracellular matrix is an amorphous gelatinous material. It is transparent, colourless, and fills the spaces between fibres and cells. It actually consists of large molecules called glycosoaminoglycans (GAGs) which link together to form even larger molecules called proteoglycans.
Nov 19, 2021 · Although acutely injured tendons attempt a healing process accompanying inflammation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, repaired tendons often contain fibrovascular scars with disorganized matrix composition, which results in inferior mechanical properties and impaired force-transmitting functions (5, 6).
Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space, creating a complex meshwork of proteins and carbohydrates called the extracellular matrix ( ECM ). A major component of the extracellular matrix is the protein collagen. Collagen proteins are modified with carbohydrates, and once they're released from the cell, they assemble into ...
Sep 01, 2011 · The skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM) plays an important role in muscle fiber force transmission, maintenance, and repair. In both injured and diseased states, ECM adapts dramatically, a property thathas clinical manifestations and alters muscle function.
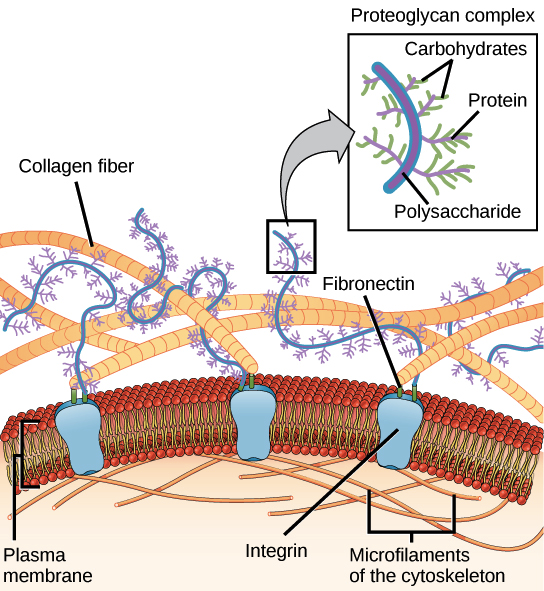
The extracellular matrix contains several adhesive fibrous glycoproteins that bind to both cells and other matrix macromolecules and, ultimately, help cells stick to the extracellular matrix. Fibronectin and laminin are the examples of best characterised large adhesive glycoproteins in the extracellular matrix.
The answer is extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix is a complex structure of macromolecules that come together to keep the cells together to form the tissues of the body. The ...
Extracellular Matrix Png Extracellular Matrix Diagram Extracellular Matrix Chart Connective Tissue Extracellular Matrix Extracellular Matrix Fibrosis Extracellular Matrix Labeled Extracellular Matrix Drawing Extracellular Matrix Location
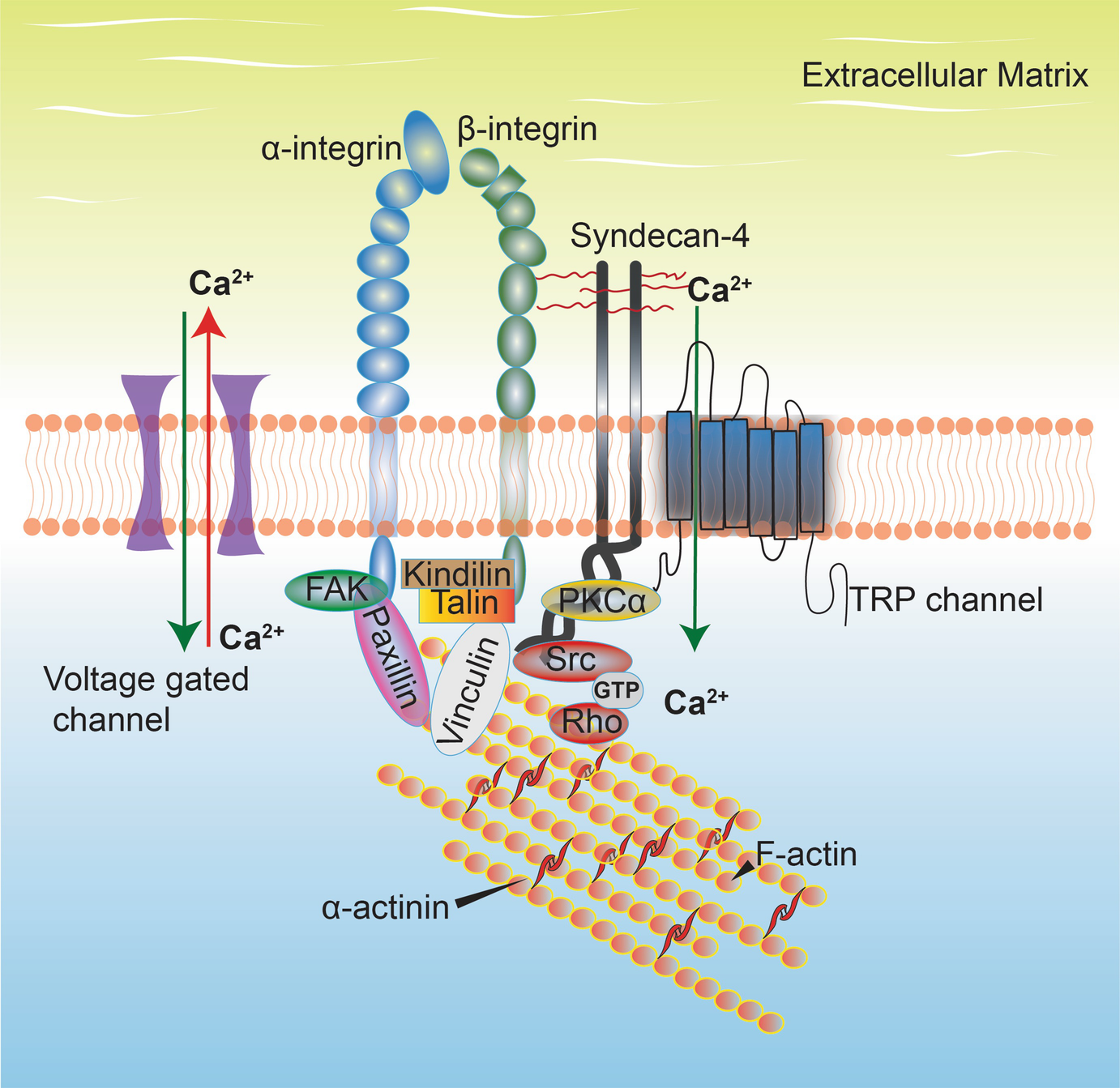
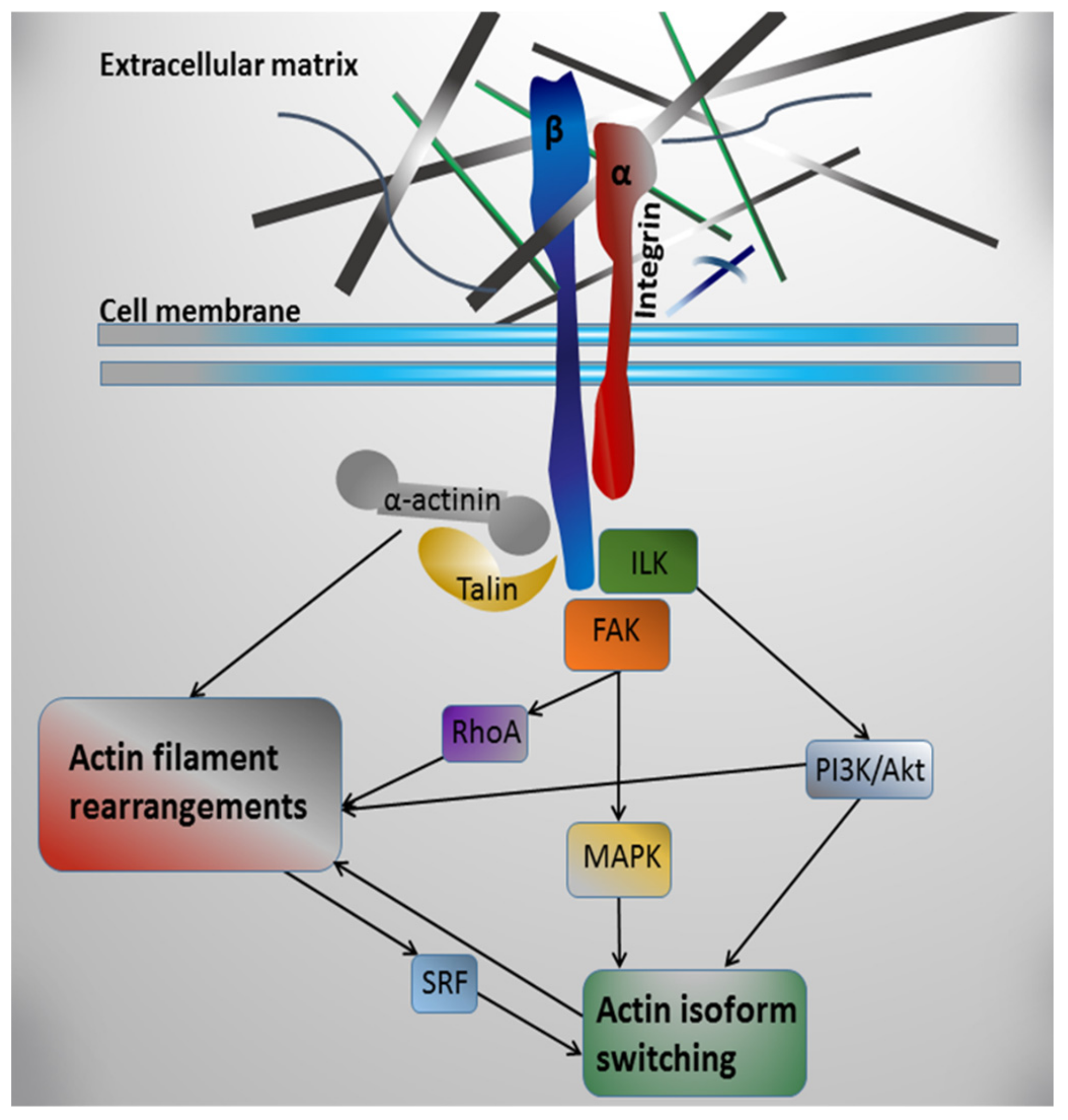
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a complex network of both structural and functional proteins assembled in unique tissue-specific architectures. The ECM provides both a mechanical framework for each tissue and organ and an inductive substrate for cell signaling. The ECM is highly dynamic and cells receive signals from the ECM and contribute to ...
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular ...

Extracellular Matrix Labeled Infographic Vector Illustration Scheme Biological Diagram With Collagen Fiber Fibronectin Canstock
The extracellular matrix of cartilage is secreted by chondroblasts, (chondro = cartilage), which are found in the outer covering layer of cartilage. As the chondroblasts secrete matrix and fibres, they become trapped inside it, and mature into cells called chondrocytes. (See diagram opposite)
Components of the basal lamina. The basal lamina consists of a mixture of collagens, laminin (glycoprotein), perlecan (heparan sulphate glycoprotein), entactin (glycoprotein). These proteins can bind to each other to make a highly crosslinked extracellular matrix as shown in this diagram.
This image illustrates the connections between the extracellular and intracellular matrix. In this diagram of the extracellular matrix (ECM) of an animal cell, which term is best represented by the letter A? Which of the following statements about the extracellular matrix (ECM) in organisms is true? The ECM is a fiber composite that provides ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
A Closer Look at the Extracellular Matrix. As seen in the diagram, components include the fibers of the ECM, glycoproteins, glycolipids, integral proteins, and peripheral proteins. In 1988, Martin Heine published his discovery that underneath the acupuncture points he studied, vessel-nerve bundles penetrate the fascia and bring a cylinder made ...
Download scientific diagram | A schematic drawing of the extracellular matrix molecular organization. The interstitial matrix is mainly composed of collagen, fibronectin, elastin, and ...
The extracellular matrix will allow this by letting these growth processes take ample opportunity to recruit extracellular proteins and minerals to build and fortify the growing skeleton. Likewise, forming scar tissue after an injury will benefit from the extracellular matrix and its rich meshwork of water insoluble proteins.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is an intricate network composed of an array of multidomain macromolecules organized in a cell/tissue-specific manner. Components of the ECM link together to form a structurally stable composite, contributing to the mechanical properties of tissues. The ECM is also a reservoir of growth factors and bioactive ...
Which of the labeled structures in the diagram consists of thick bundles of collagen fibers that extend into the extracellular bone matrix and numerous osteoblasts for growth in diameter of the bone? F. Where in the diagram is the metaphysis? B.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is the non-cellular component present within all tissues and organs, and. provides not only essential physi cal scaffolding for the cellular constituents but also ...
Cytoskeletal fences (corrals) and binding to the extracellular matrix. Some proteins embedded in the bilipid layer interact with the extracellular matrix outside the cell, cytoskeleton filaments inside the cell, and septin ring-like structures. These interactions have a strong influence on shape and structure, as well as on compartmentalization
The Extracellular Matrix. The extracellular matrix (ECM) is made up of 3 main elements: Aggrecans (10%) Water (75%) Collagen fibres and other constituents (15%) Aggrecans are proteoglycans which is a molecule made up of carbohydrates (repeating disaccharide units known as glycosaminoglycans or GAGs) attached to a protein core.
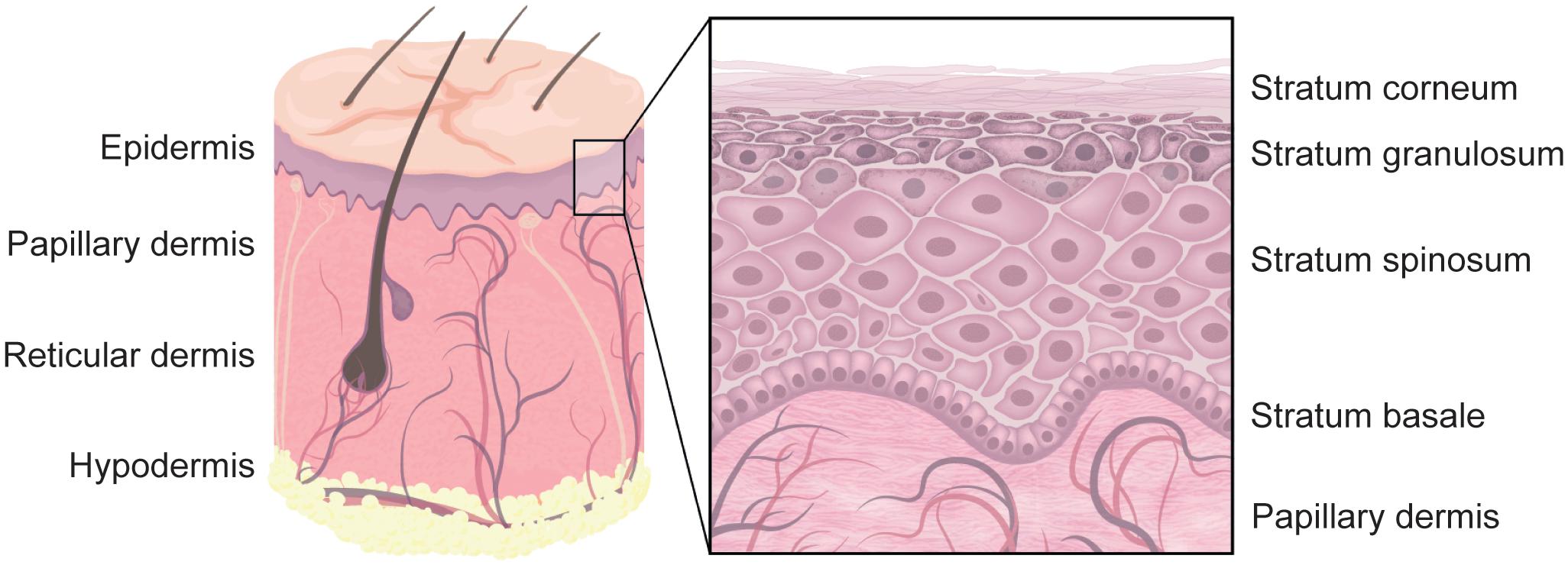
Frontiers The Extracellular Matrix In Skin Inflammation And Infection Cell And Developmental Biology
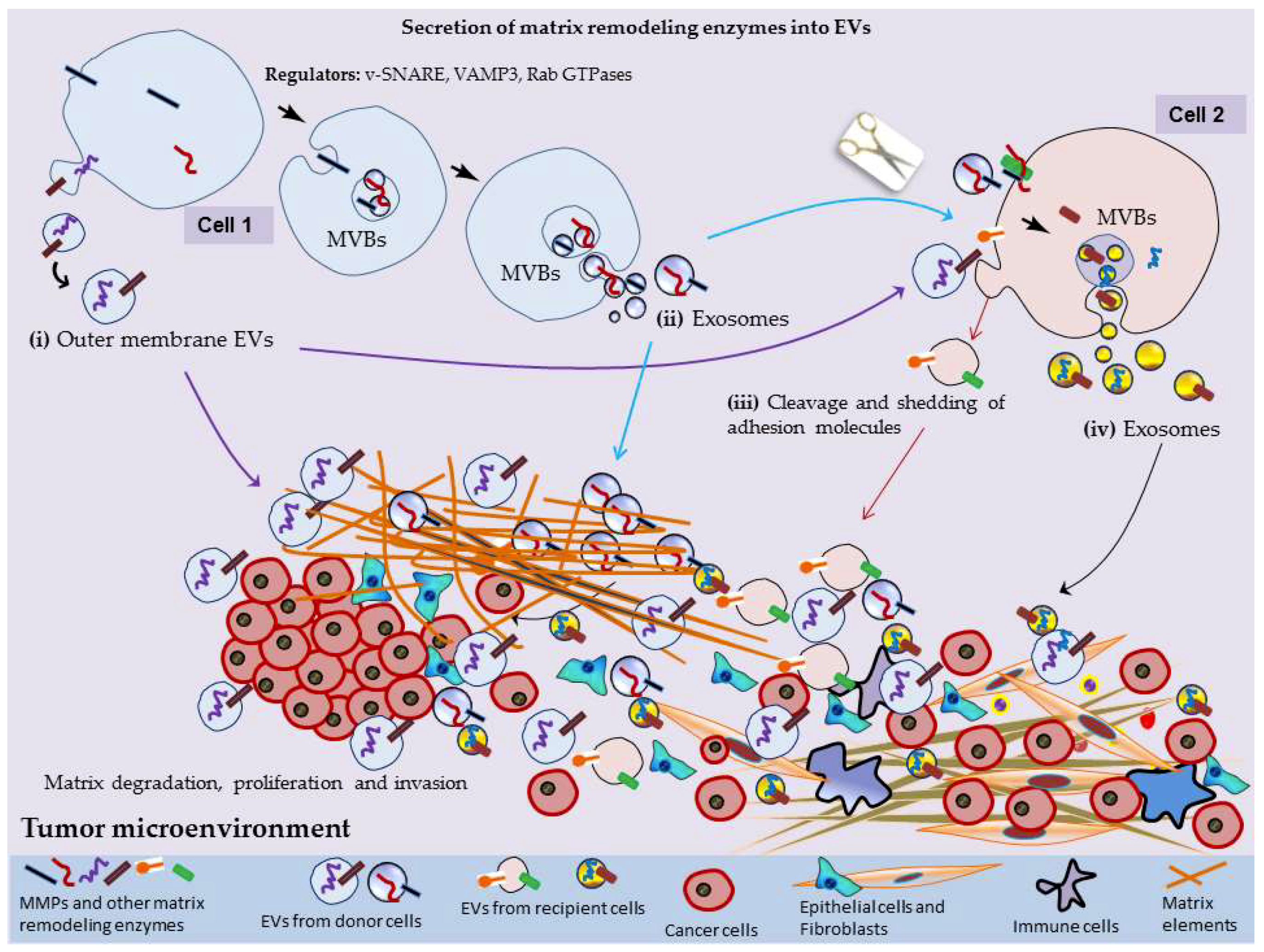
Cells Free Full Text Extracellular Vesicles And Matrix Remodeling Enzymes The Emerging Roles In Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Progression Of Diseases And Tissue Repair Html

The Extracellular Matrix As A Multitasking Player In Disease Theocharis 2019 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
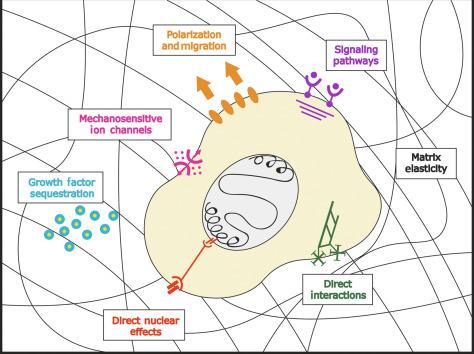
The Physical And Biochemical Properties Of The Extracellular Matrix Regulate Cell Fate Center For Bioengineering Tissue Regeneration
Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring And Plant Cell Organelles Cake Parts Of The Animal Cell Animal Cell Model Diagram Project Parts Structure Labeled Coloring And Plant Cell Organelles
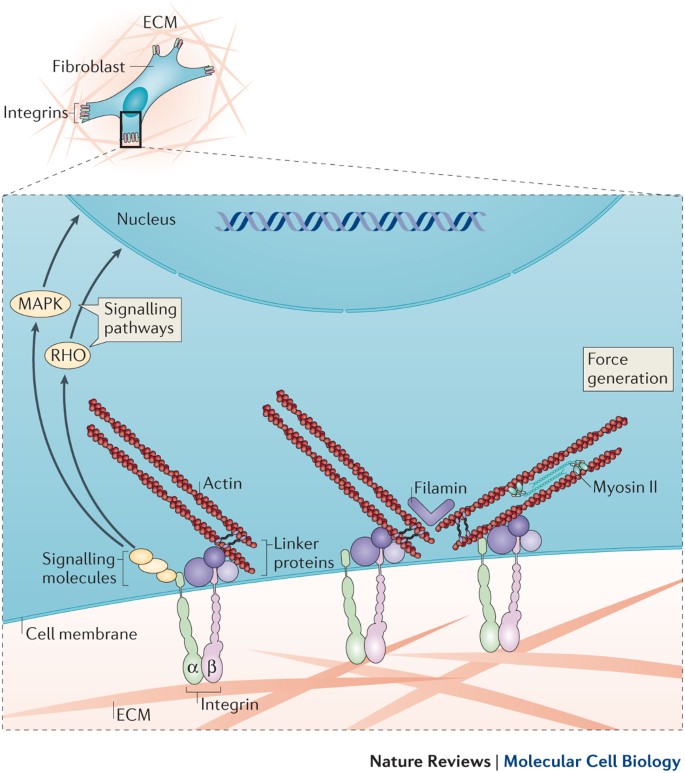























Comments
Post a Comment