38 free energy reaction coordinate diagram
by JM Scholey · 2013 · Cited by 6 — Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to relate the free energy changes that occur during the progress of chemical processes to the rate and ... A AG+ B AG+ Free Energy Reaction coordinate a) The diagram could represent different Sn1 reactions. Plot A represents the tertiary alkyl halide and plot B an allylic alkyl halide. b) The diagram could represent the addition of HCl to propene. Plot A
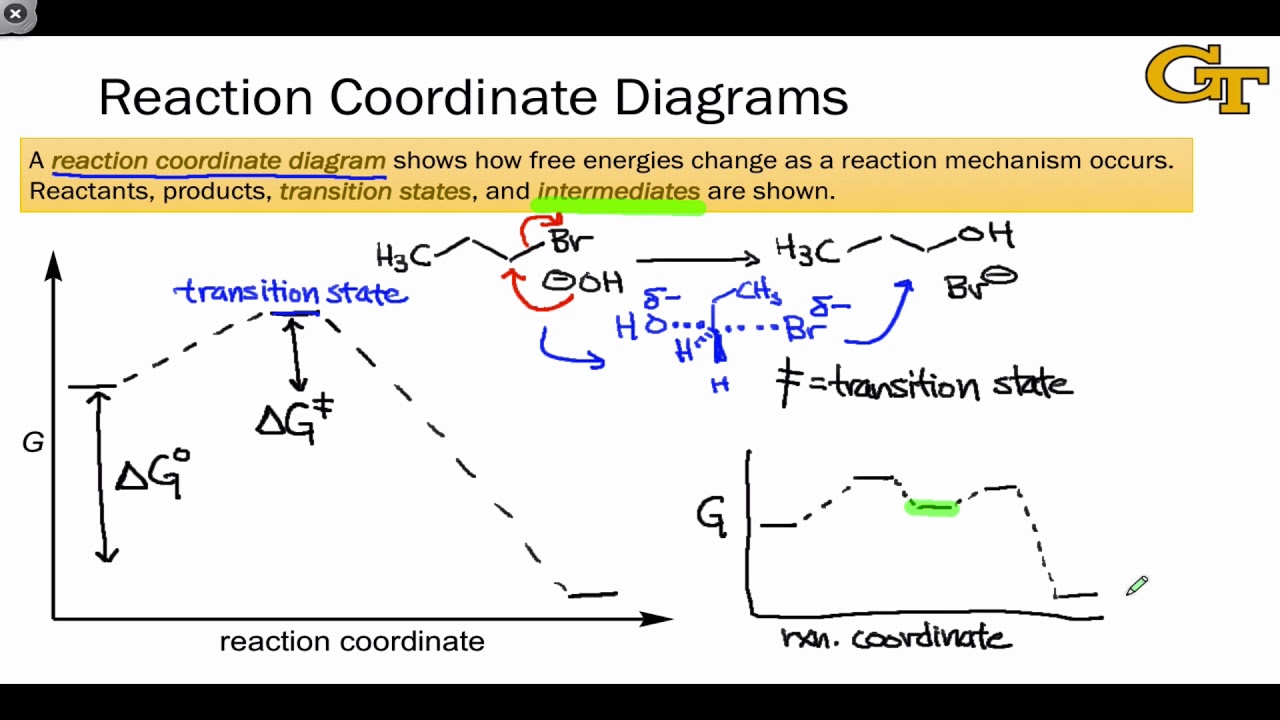
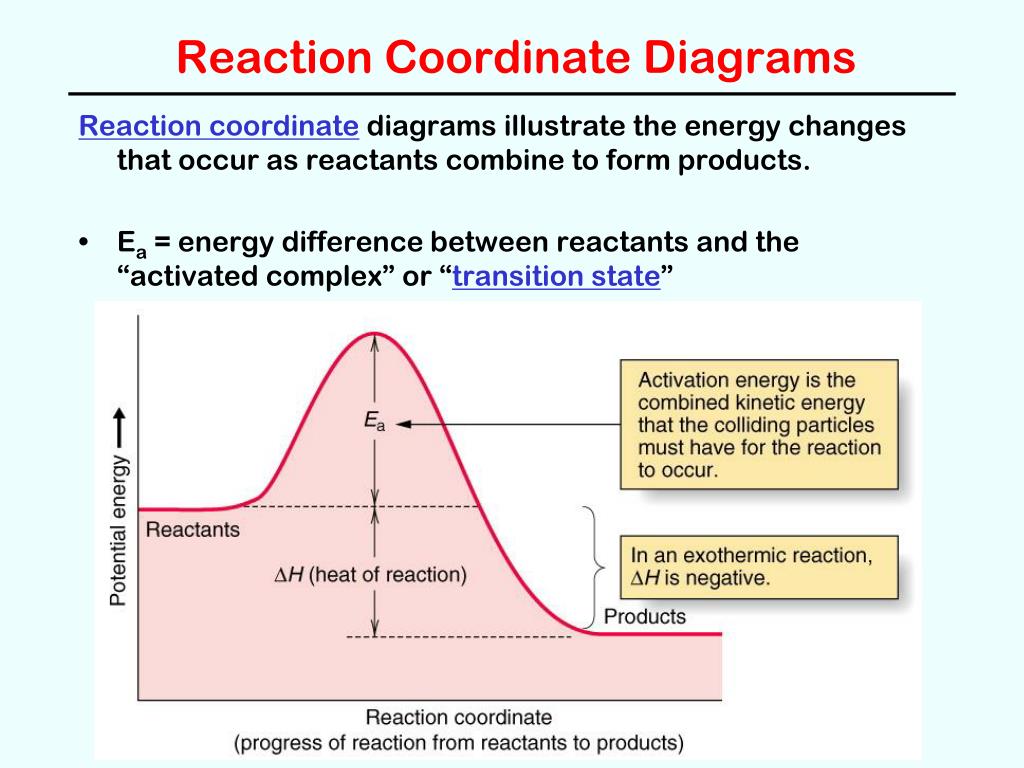
Free-energy diagrams, or reaction coordinate diagrams, are graphs showing the energy changes that occur during a chemical reaction. The reaction coordinate represented on the horizontal axis shows how far the reaction has progressed structurally.

Free energy reaction coordinate diagram
Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a ... A general Reaction Coordinate Diagram relating the energy of a system to its geometry along one possible reaction pathway is given in the figure below. In the figure below, the Activation Energy, Ea is that critical minimum energy in a chemical reaction required by reactants to be converted into products. the quantities, Ea; Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol-1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol-1).
Free energy reaction coordinate diagram. Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction . This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram. positions of atoms during a reaction. Reaction coordinate Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction. - A maximum on an energy diagram. • Activation Energy, ∆G‡: The difference in Gibbs free energy between reactants and a transition state. Biochemical standard free-energy change ΔG'° is the standard free-energy change at pH 7.0. Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 1) Free Energy of activation for B-> A is E Answer- E 2) Option …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: What is the free energy of activation for reaction B A in the following reaction coordinate diagram? Reaction Coordinate Question 16 0.5 pts Which of the following carbocations is the least stable? CH3 1 CHỊCH IV.
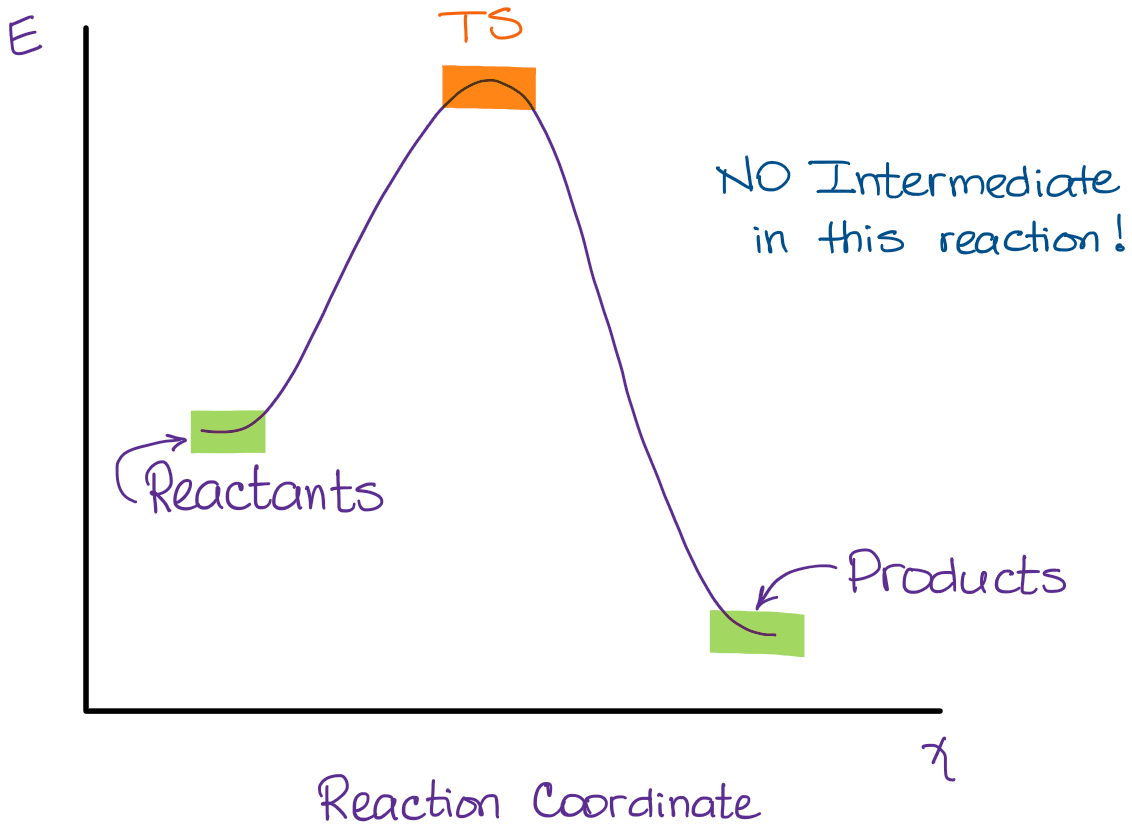
This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f... 5.3. Reaction coordinate diagrams. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ' reaction coordinate ', tracing from left to right the progress of ... A chemist draws a reaction coordinate diagram for a reaction based on the knowledge of free energy or enthalpy change associated with the transformation which helps him to place the reactant and product into perspective and whether any intermediate is formed or not. A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change there are many ENDOTHERMIC reactions such as photosynthesis that occur.! An Exothermic (Exergonic) Reaction! 2 C 8 H 18 + 25 O 2 → 16 CO 2 + 18 H 2 O! A reaction with ∆H°0 is endothermic.
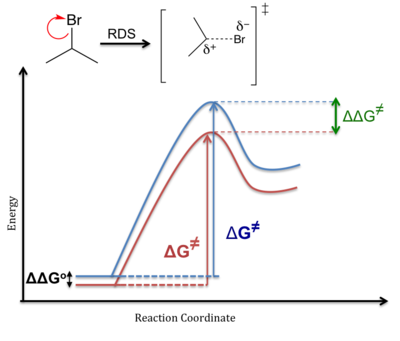
The reaction free-energy diagram in Fig. summarizes these ideas. The first step, ion-ization of the alkyl halide to a carbocation, is the rate-limiting step and thus has the transition reaction coordinate Br Figure Reaction free-energy diagram for the S. Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo): a measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state ... Energy Surfaces vs. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Something that cannot be represented in the three dimensional energy surface below is the differentially populated vibrational modes of the molecules Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to simplify the situation, they represent a composite Reaction coordinate Transition state ΔG 1 ‡ ΔG 1 ‡' ΔG -1 ‡' ΔG -1 ‡ ΔG° G A G P Initial state Final state Fig. 4.2 A free energy (G) diagram for a simple reversible exothermic reaction A↔P(solid and broken lines). G A and G P represent the average free energies per mole for the reactant A and the product P, the initial and ...
Reaction coordinate diagrams for exergonic and endergonic reactions. In the exergonic reaction, the reactants are at a higher free energy level than the products (reaction goes energetically downhill). In the endergonic reaction reaction, the reactants are at a lower free energy level than the products (reaction goes energetically uphill).
Indian Institute of Science. I am adding here a MATLAB code for drawing free energy reaction profile. This is just for plotting del Grxn vs reaction coordinate. (A small change is needed to ...
In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the 'reaction coordinate', tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. The energy diagram for a typical one-step reaction might look like this:
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Diagram of a catalytic reaction, showing the energy niveau depending on the reaction coordinate. For a catalysed reaction, the activation energy is lower. In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway.
The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram.
The reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction plots the changes in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) during the conversion of reac-tants (R) to TS to products (P; Figure 1B). It can be seen that P is of lower free energy than R, so this reaction is thermodynamically fa-vorable, that is, it proceeds in the direction of P with the release of
ΔGrxn = ΔH rxn − T ΔSrxn So, the reaction is necessarily endothermic, and the reaction coordinate diagram and potential energy diagram look similar. The main difference is again, you'd be using ΔH rxn instead, and your y-axis would be the potential energy, NOT the Gibbs' free energy. Answer link
A reaction coordinate diagram is a graph that plots energy versus reaction progress. The amount of energy that needs to be added is called the activation energy, which is the point where the line ...
Right off the bat, we can see that the free energy of the products is greater than that of the reactants. Thus, this reaction has a positive change in free ...
1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed.
We can illustrate this through a "potential energy diagram" (often called a ... The "reaction coordinate" (the X axis) is the collection of bond length, ...
reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with
For this quiz, you must be able to: Understand endothermic and exothermic reactions. Identify which points on sample reaction coordinate diagrams represent the activation energy and the change in ...
Fig. 1.1: Free energy vs Reaction coordinate diagram for above reaction . 1.1.2 Definition of Thermodynamic Terms: 1.1.2.1 System: It is defined as any portion of the universe or the quantity of matter that chosen separately from the rest of the universe & closed by boundary surface.
Gibbs free energy reaction coordinate profiles found in some textbooks. The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the ...
Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol-1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol-1).
A general Reaction Coordinate Diagram relating the energy of a system to its geometry along one possible reaction pathway is given in the figure below. In the figure below, the Activation Energy, Ea is that critical minimum energy in a chemical reaction required by reactants to be converted into products. the quantities, Ea;
Let's consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants, A, is transformed into a product or set of products, B. The diagram below is called a ...















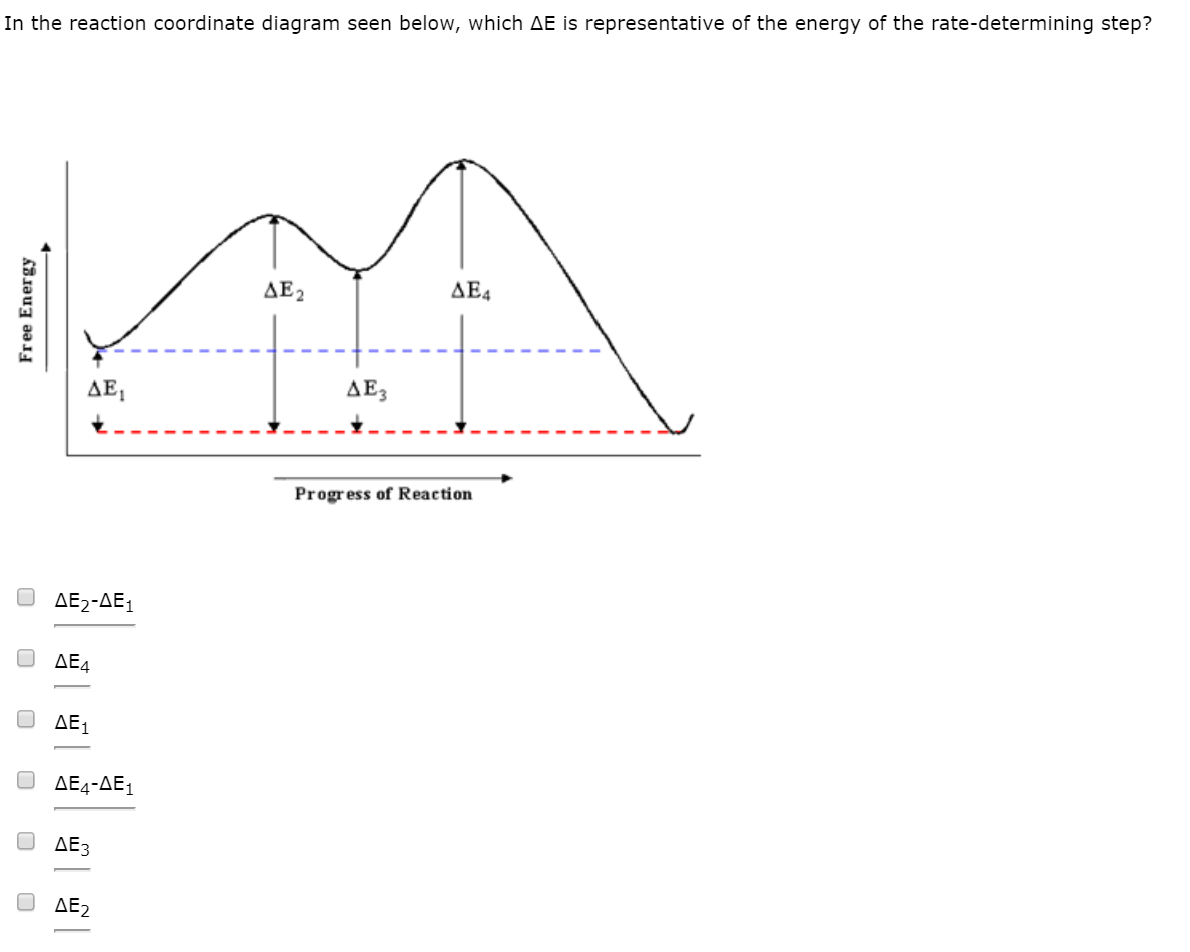

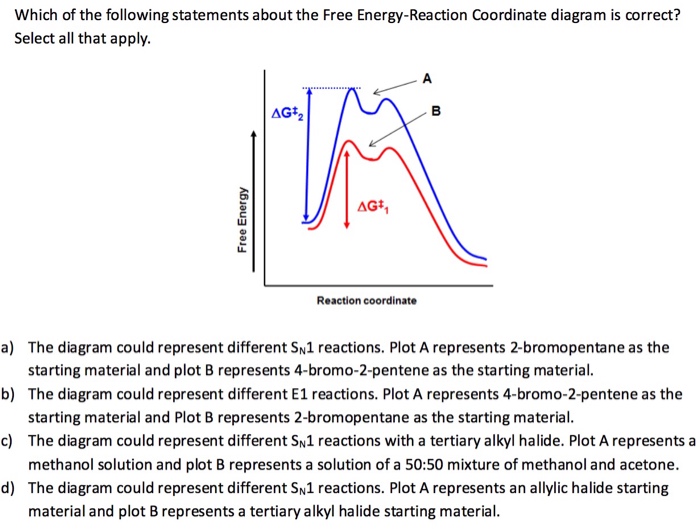
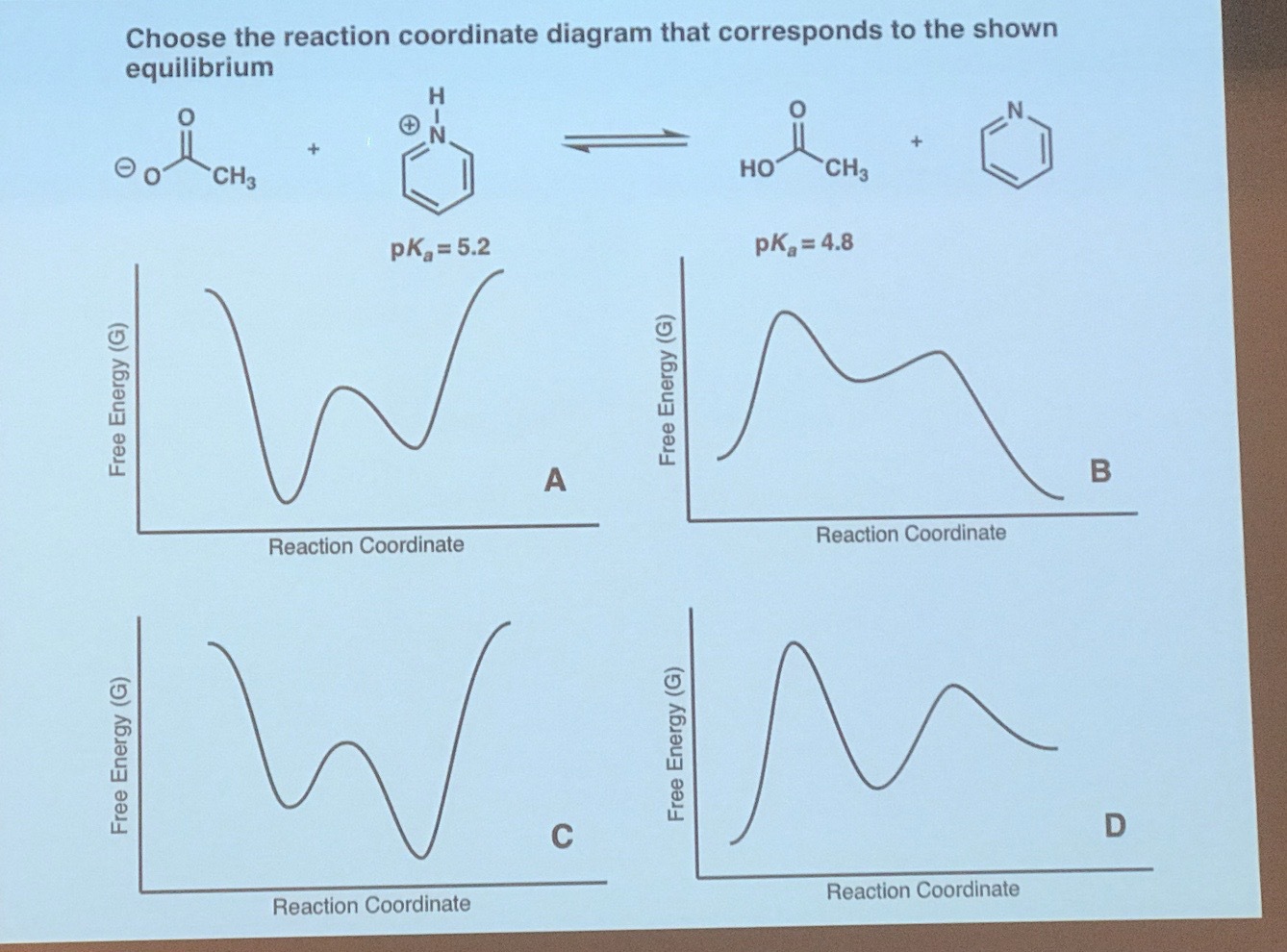
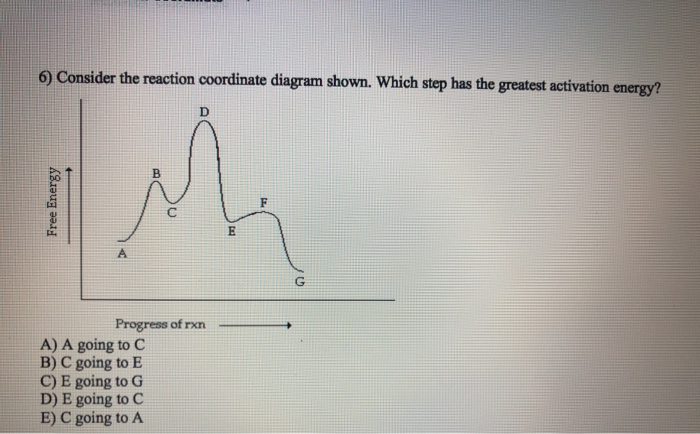




Comments
Post a Comment