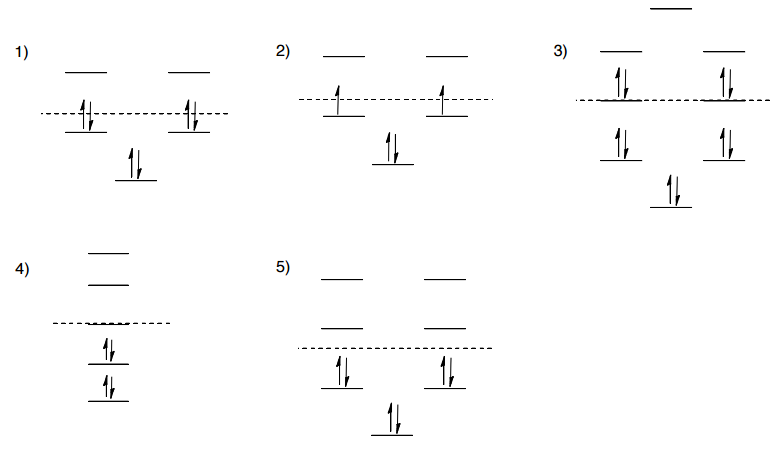
38 molecular orbital diagram practice
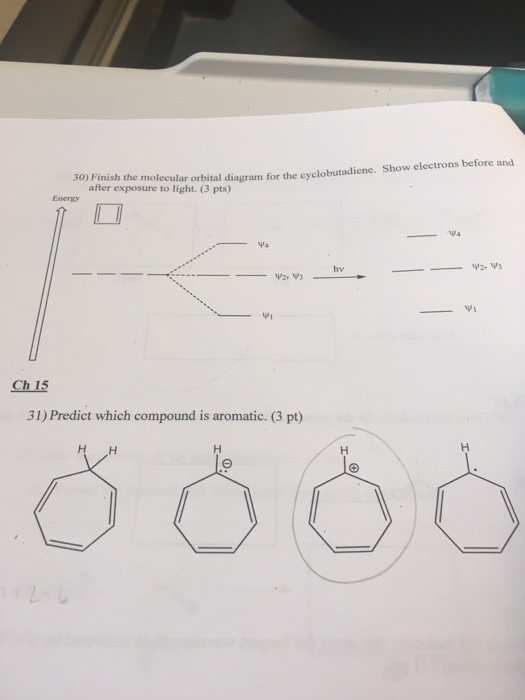
01 Reviewing Atomic Orbitals, Electron Configurations and Lewis Diagrams . 02 Molecular Orbitals of Homonuclear Diatomics . 03 Molecular Orbitals of Heteronuclear Diatomics . 04 Molecular Orbitals of Polyatomic Molecules. 05A Band Theory and Bonding in Metals. 05B Valence Bond Theory. 06 Entropy and Free Energy. 07 Free Energy and Equilibrium note that from our N pz orbitals we will obtain N π orbitals. Further, each carbon atom has one free valence electron to contribute, for a total of N electrons that will need to be accounted for (assuming the molecule is neutral). Accounting for spin, then, there will be N/2 occupied molecular orbitals and N/2 unoccupied ones. For the ground
Molecular orbital Diagram Practice. molecular orbital diagrams of diatomics worksheet in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule in this theory each ...

Molecular orbital diagram practice
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in 📗 Need help with chemistry? Download 12 Secrets to Acing Chemistry at http://conquerchemistry.com/chem-secrets/💯 If you like my teaching style and are inte... Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B 2. The number of unpaired electrons in the B 2 molecule is _____. (a) zero (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4 8. Which one of the following statements is false? (a) Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory can be described as two different views of the same thing.
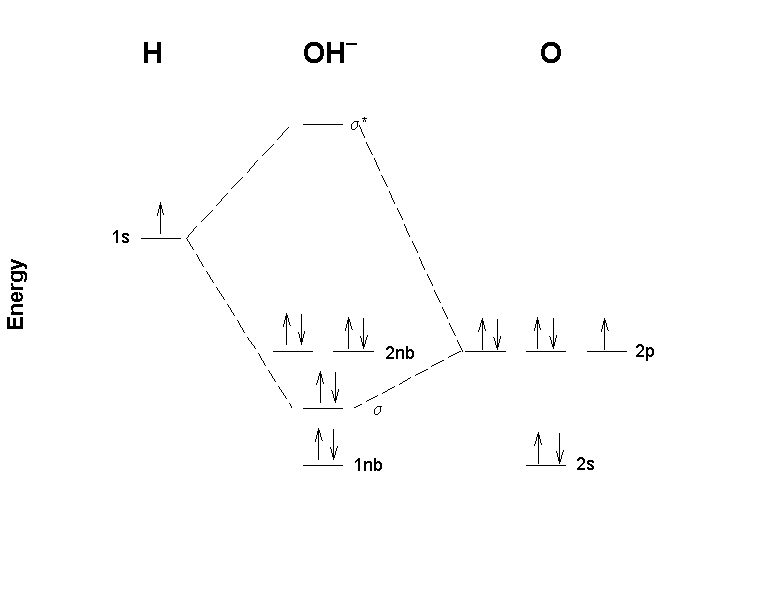
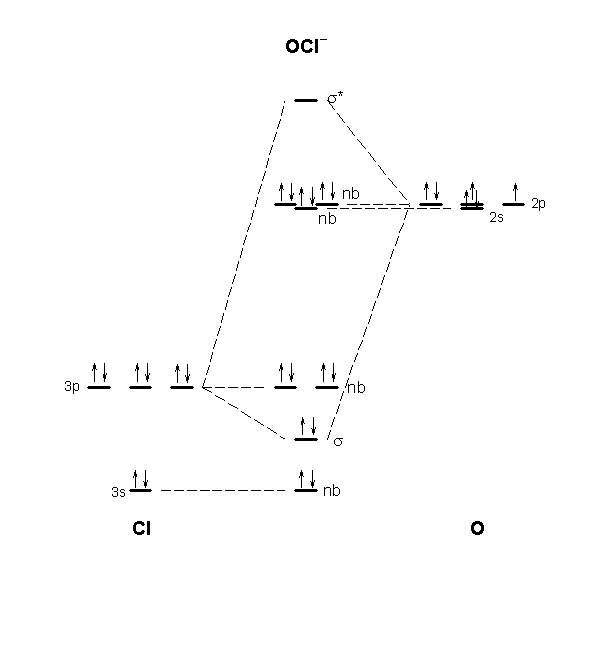
Molecular orbital diagram practice. Practice Problems Molecular Structure and Covalent Bonding. 1. Write Lewis structures for (a) XeF 4, (b) ... Draw a molecular orbital diagram for the hypochlorite ion. What is the bond order? Is this consistent with the bonding predicted by a Lewis dot structure? 17. Draw a molecular orbital diagram for the hydroxide ion. The molecular orbital diagram for ClO - is given below: The basis orbitals for Cl are 3s and 3p and for O are 2s and 2p. Z* for O 2s and 2p orbitals are similar so the AOs start at nearly the same energy. For the Cl 3s and 3p orbitals the two Z* values are quite different so the initial energies are more separated. Molecular Orbital Diagram Practice . By Marsha Massey. University of Sydney has created a practice website for reviewing different parts of molecular orbital diagrams. Using this resource you can add pieces to pre-drawn MO diagrams for over 20 different molecules. In this video, we do some practice with the molecular orbitals of molecules by linear combinations of 2s and 2p orbitals. Remember, there is one 2s orbital ...
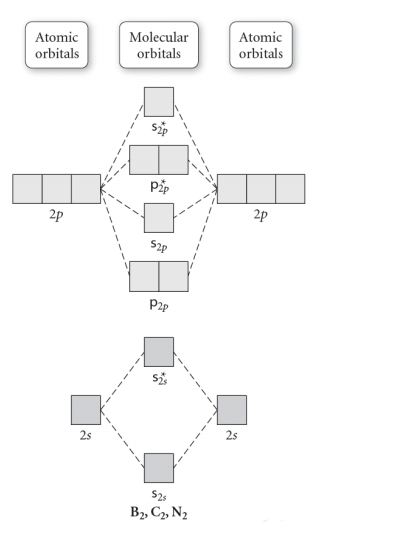
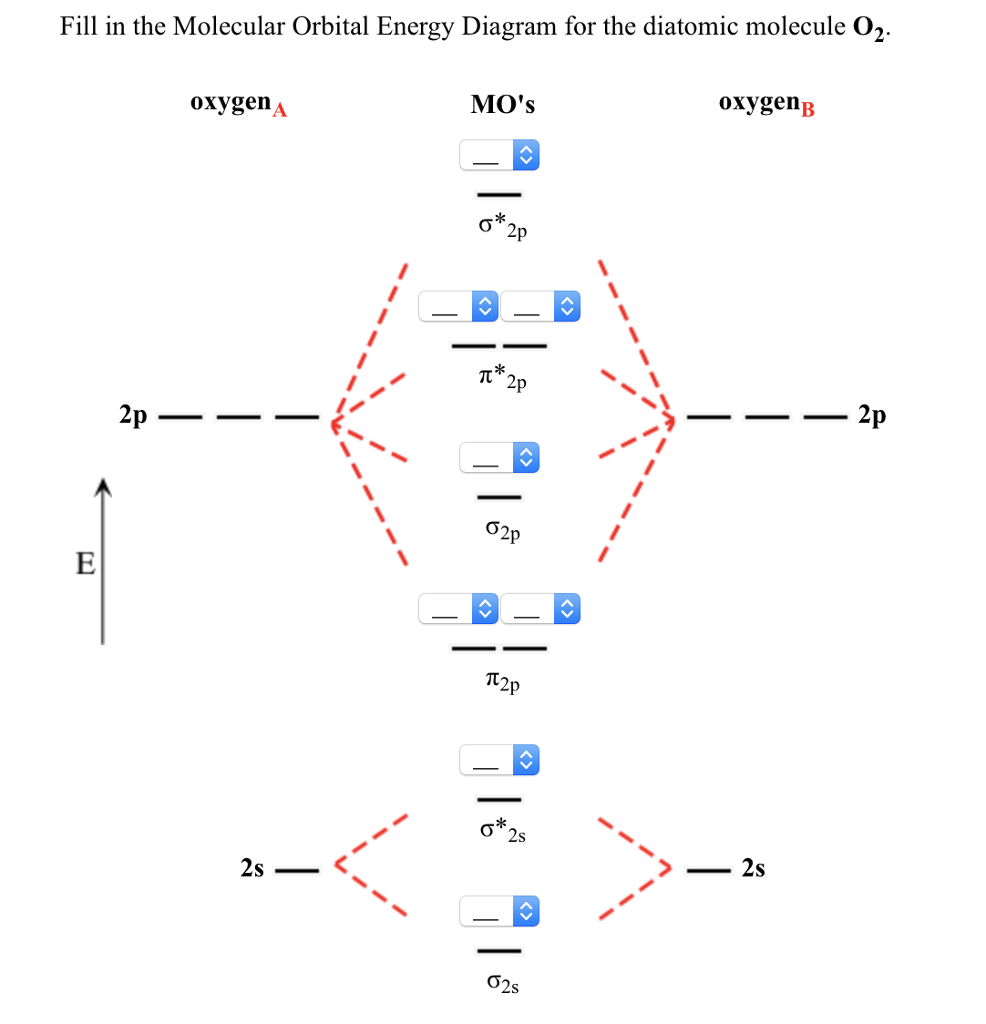
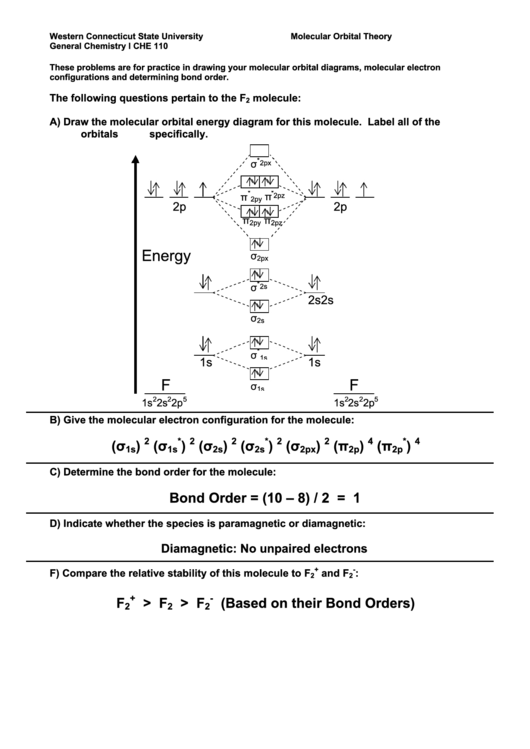
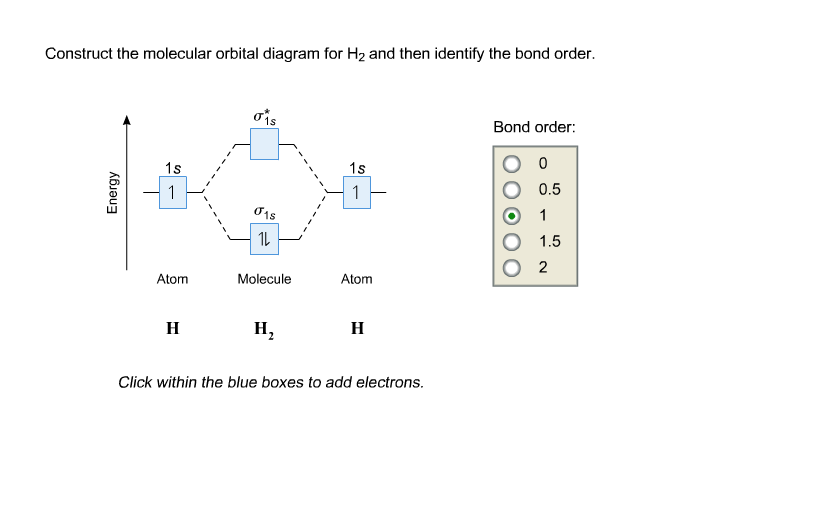
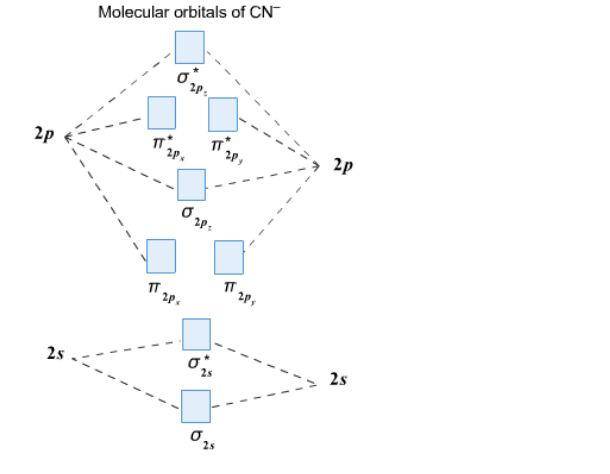
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... These problems are for practice in drawing your molecular orbital diagrams, molecular electron configurations and determining bond order. The following questions pertain to the F2 molecule: A) Draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for this molecule. Label all of the orbitals specifically. *2px Here are some boxes for you to practice drawing s orbitals in, although you do not really need boxes. As we proceed developing atomic and molecular orbit- ... For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2. ATOMIC ORBITALS 2p x 2p y 2p z l = 1 x y z n = 2 This is an accurate representation of a 2p x orbital. This is a common ... Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.
Molecular Orbital Theory Practice Questions. Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises. Sketch the distribution of electron density in the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals formed from two s orbitals and from two p orbitals. How are the following similar, and how do they differ? (a) σ molecular orbitals and π molecular orbitals ... Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 . Molecular Orbital Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules . 1. (a) 1The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠, so 𝐻𝐻 has 1 valence electron. The electron configuration for 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 is 1𝑠𝑠2, so 𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻 has 2 valence electrons. We are being asked to determine the molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms.. Recall: In the molecular orbital theory, electrons are seen as being delocalized or spread out over a molecule instead of concentrated in a covalent bond.. A bonding orbital is a region of high electron density between nuclei where a bond forms; An anti-bonding orbital is a region that has ... VSEPR theory (molecular shapes), bond polarity, molecular polarity and IMFs ... 213XZ948 Felicia Mo AP Chemistry Unit 2,3 Question #1 1a) 1b) C2H2 ... There are 60 multiple-choice questions and 7 free- response questions.. orbitals (called molecular orbitals) spread over entire molecule.
Practice: Orbital diagrams (tutorial also) Molecules and Compounds [Nomenclature] (Chapter 5) Practice: % comp, emperical/molecular formula worksheet ; Virtual. Mg 1s 22s2 2p6 3s 2. You can choose which wavefunction you would like to see from the • A maximum of 20 orbitals can be listed in the Orbital drop-down list.
Chapter 11 Answers Practice Examples 1a. There are three half-filled 2p orbitals on N, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each half-filled 2p orbital from N will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I. Thus, there will be three N—I bonds. The I atoms will be oriented in the same direction as the three 2p orbitals of N: toward the x ,y, and z-directions of a Cartesian coordinate ...
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
About Molecular Practice Orbital Worksheet Diagram . 30) The molecular geometry of the PF4+ ion is _____. Draw a complete molecular orbital diagram for the conjugated. (a) Construct a molecular orbital energy level diagram for this species. When naming these compounds prefixes are used to denote how many of each atom is bonded in the compound.
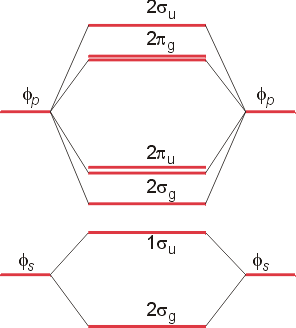
Using Symmetry: Molecular Orbitals One approach to understanding the electronic structure of molecules is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Molecular orbital Diagram Practice. molecular orbital diagrams of diatomics worksheet in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule in this theory each ...
Practice determining the hybridization for atoms in covalent compounds. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ...
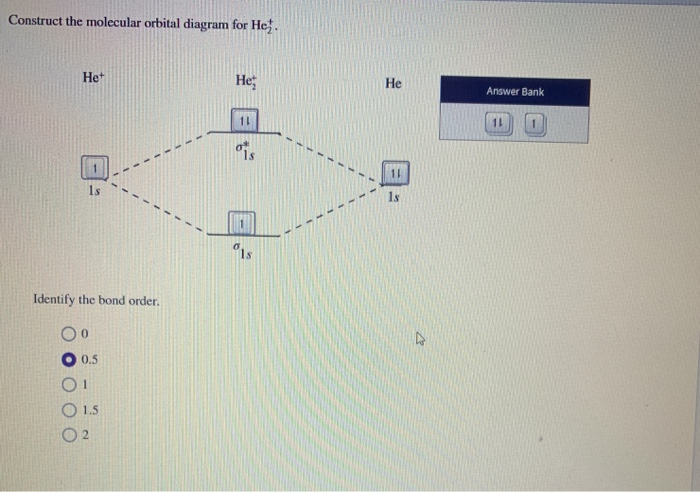
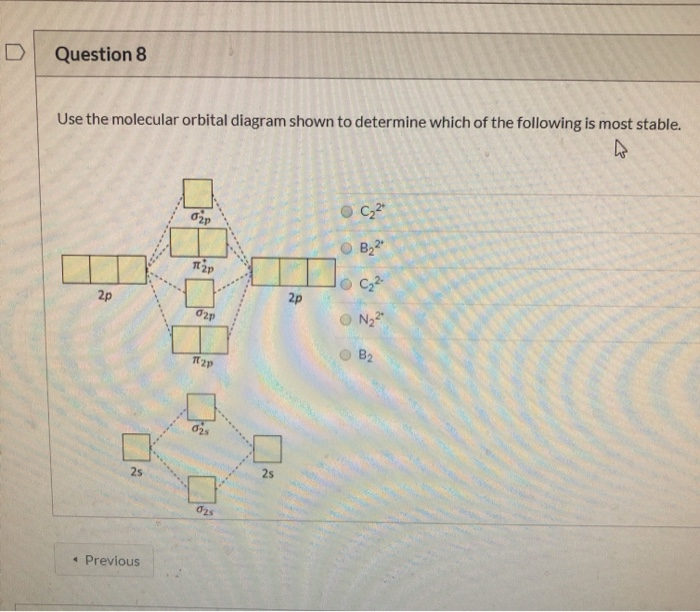
By constructing a molecular orbital picture for each of the following molecules, determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. a. B 2 b. C 2 c. O 2 d. NO e. CO a. B 2 is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons, one in each of its p orbitals. b. C 2 is diamagnetic because all of its electrons are paired.
Molecular orbital Diagram Practice. molecular orbital diagrams of diatomics worksheet in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule in this theory each molecule has a set of molecular orbitals ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B 2. The number of unpaired electrons in the B 2 molecule is _____. (a) zero (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4 8. Which one of the following statements is false? (a) Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory can be described as two different views of the same thing.
📗 Need help with chemistry? Download 12 Secrets to Acing Chemistry at http://conquerchemistry.com/chem-secrets/💯 If you like my teaching style and are inte...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in















Comments
Post a Comment