43 angiosperm flower diagram
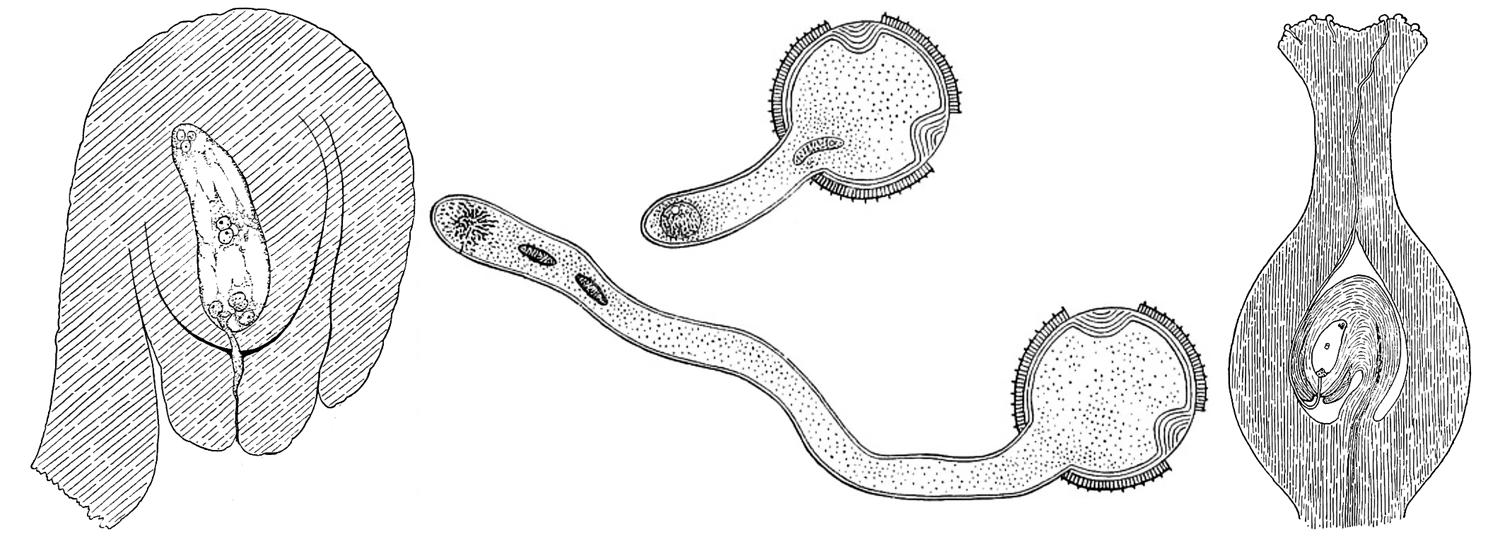
Angiosperm embryo sac diagram. Schematic drawing of the mature eight-nuclei female gametophyte (or embryo sac) in a typical angiosperm flower ovule. All eight nuclei shown are haploid. In double fertilization, the egg cell will fuse with a sperm nucleus to form a diploid zygote while the two polar nuclei will fuse with the second sperm nucleus ... 10.10.2021 · Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants MCQ Chapter 2. Below are some of the very important NCERT Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants MCQ Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 with Answers. These Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants MCQ have been prepared by expert teachers and subject experts based on the latest syllabus and pattern of term 1 and …
In this tutorial, we have discussed ‘Angiosperm Plant Families and their Floral Formula‘. Flowering plants are described in sequential order of morphological characters, like habit, habitat, root, stem, leaves, inflorescence, flower, fruit, and seed of the plant.On the basis of floral characters, a floral diagram and a floral formula are drawn.
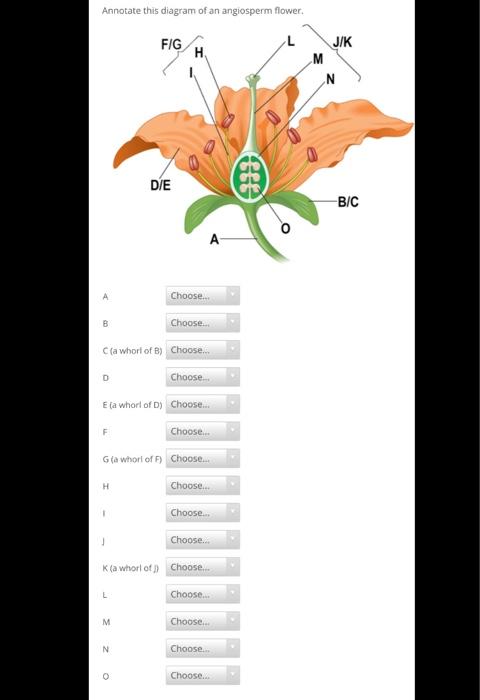
Angiosperm flower diagram
General Structure of Seed (With Diagram) | Angiosperms | Botany. A typical matured seed of angiosperms consists of two parts: 1. Seed Coat 2. Kernel. 1. Seed Coat: Seed coat is the protective covering of seed, developed from integument of the ovule. A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, ... Diagram of flower parts. Parts ... Recently discovered angiosperm fossils such as Archaefructus, along with further discoveries of fossil gymnosperms, suggest how angiosperm characteristics may have been acquired in a series of steps. An early fossil of a flowering plant, Archaefructus liaoningensis from China, is … Flowers with five parts per whorl are a synapomorphy for the Pentapetalae, a large clade that includes most eudicots (= Superrosids + Superasterids; see the diagram at the bottom of this page). Floral parts in multiples of three, typical of monocots, might be the ancestral angiosperm condition (see here ).
Angiosperm flower diagram. Floral symmetry describes whether, and how, a flower, in particular its perianth, can be divided into two or more identical or mirror-image parts.. Uncommonly, flowers may have no axis of symmetry at all, typically because their parts are spirally arranged. Parts of a Flower Diagram . The flower is the structure the plant uses for reproduction. The sepals protect the flower before it opens. The petals attract pollinators. The anthers of the stamens (male) produce pollen. The ovules of the pistil (female) produce eggs. Pollination is the movement of pollen from the male to the female. 06.06.2007 · Diagram illustrating the tissue layers and their organization within monocot and dicot roots. ... Monocots have their flower parts in threes or multiples of three; example the tulip and lily (Lilium ). Dicots have their flower parts in fours (or multiples) or fives (or multiples). Examples of some common dicot flowers include the geranium, snapdragon, and citrus. Monocot (left) and … they are angiospermic or flowering plants which are characterised by the presence of two cotyledons in the seed, generally reticulate venation in leaves (with a few exceptions), concentric tissues in the stem with open vascular bundles arranged in a ring, penta- or tetramerous flowers e.g., pea, rose, eucalyptus, mustard, cotton, acacia, …
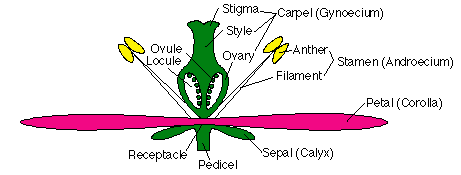
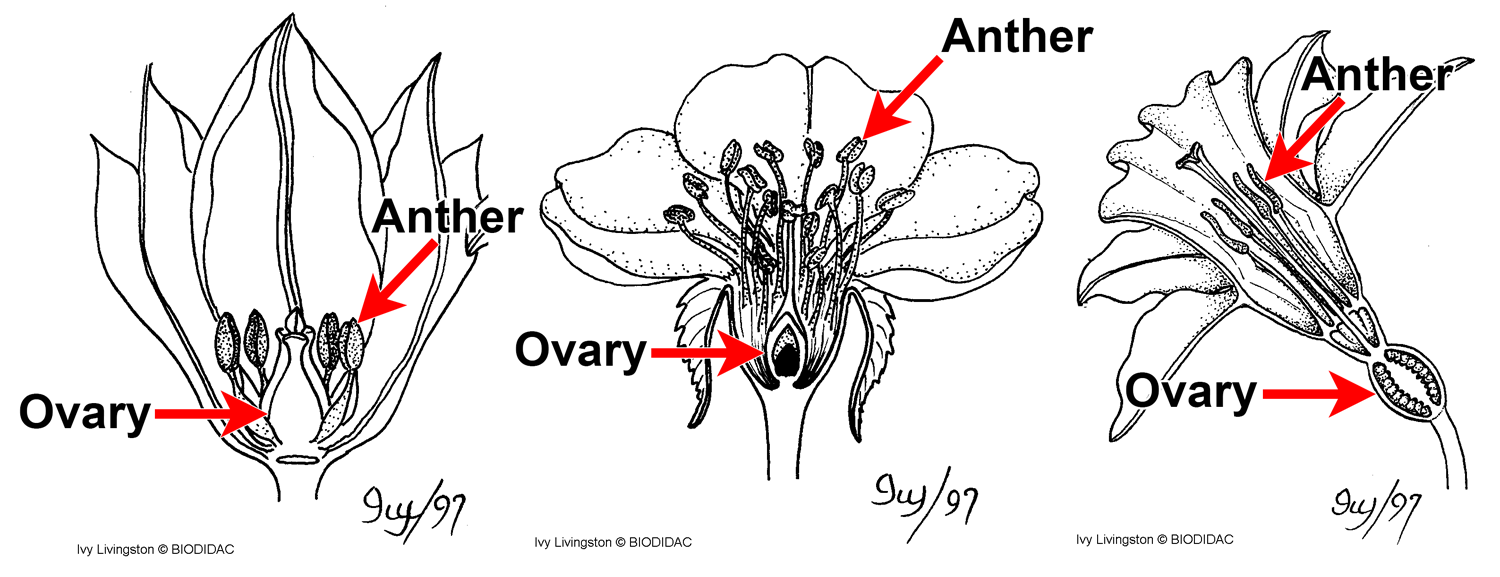
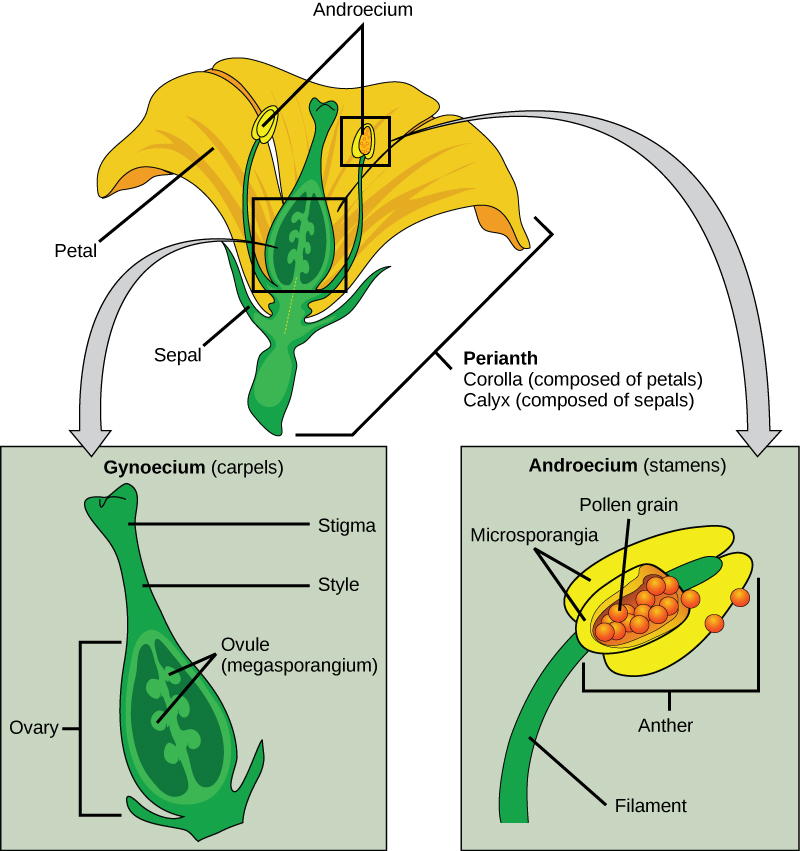
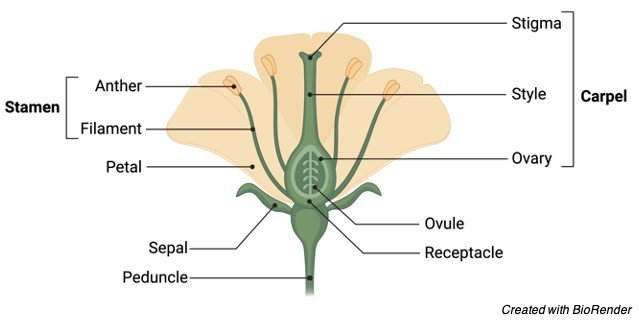
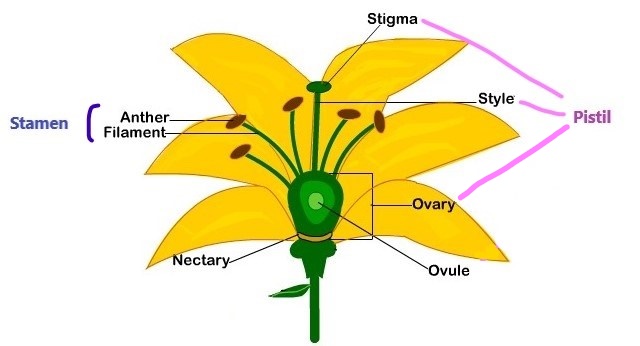
American Journal of Botany (AJB) is an internationally renowned journal publishing innovative, significant research of interest to a wide audience of scientists in all areas of plant biology (including ecology, evolution, physiology, biodiversity, systematics, development, genetics, paleobotany, structure and function), all levels of organization (ecosystem to molecular), and … 3. Introduce flower structure. Refer children to the flower diagram chart. Explain that each flower is unique with its own special beauty. While flowers are composed of the same Location: classroom with tables for children to work in small groups Objectives: Learners will 1) identify the different parts of a flower and understand their function. 1 Label a diagram of the external parts of a typical flowering plant Shoot, root, stem, leaves, flower, fruit, seed. 2 State the function of the root and shoot 3 Identify tap and fibrous root systems 4 Explain the term Meristem and give its location in the stem and root 5 Name and give the function of four zones in a longitudinal section of a root The stamen is the male part of a flower. In a flower diagram, stamen are located on both sides of the pistil. The stamen consists of two parts: Anther: The anther is the head of the stamen. It produces pollen. Filament: The filament is the stalk attached to the flower that holds the anther. The stamen's function is to produce male reproductive ...
The petals of a flower are often brightly colored and scented to attract insects and other pollinators. The stamen is the male part of the plant. It is composed of the filament (a stalk) that holds the anther, which produces the pollen. Pollen is needed for plants to produce seeds. The carpel is the female part of the flower. The top part of the carpel contains the stigma. The style … Hi there! 🐐 Below is a massive list of flower words - that is, words related to flower. There are 500 flower-related words in total, with the top 5 most semantically related being blossom, bloom, pollen, sunflower and orchid.You can get the definition(s) of a word in the list below by tapping the question-mark icon next to it. 18 Feb 2016 — The stamen is the male reproductive structure of a flower. It consists of a stalk-like filament that ends in an anther. · The pistil, or carpel ... The characteristics of flowering plants or angiosperms that sets it apart from gymnosperms are four sets of organs. These organs are - Sepals. Petals. Stamens. Carpels. The diagram below illustrates each of these parts of a flower - I m a g e w i l l b e U p l o a d e d S o o n
5 Mar 2021 — Although they vary greatly in appearance, all flowers contain the same structures: sepals, petals, carpels, and stamens. The peduncle attaches ...
Figure 2: Diagram of a tomato flower and its fruit. The ovary within the flower develops into a tomato fruit that we eat. The petals, stamens, and stigma dry up and fall off as the fruit matures. Source: Adapted from Portions for Elves . The tomato flower consists of four main parts: Sepal: This part of the flower, which is green in colour, is first visible when the bud forms. It protects …
09.08.2019 · Summary diagram for the life cycle of an angiosperm. The diploid (2n), multicellular sporophyte bears flowers. Embryo sacs (megagametophytes) develop in the ovules, which are found in the ovary. Pollen grains (microgametophytes) develop in the pollen sacs (microsporangia) of the anther. One megaspore mother cell occurs in each ovule; it undergoes …
Flowering plants, the angiosperms , were the last of the seed plant groups to evolve, appearing over 100 million years ago during the middle of the Age of Dinosaurs (late Jurassic ). All flowering plants produce flowers and if they are sexually reproductive, they produce a diploid zygote and triploid endosperm .
LAB 15 ANGIOSPERMS updated August 15, 2003 About this site Links Related Information Assignment Reminder: Bring one flower and one fruit with you to the Angiosperm lab. Where to collect a flower and fruit? Related Information
Flower is basically a shoot which has been modified in angiosperms for carrying out the process of sexual reproduction. A flower has a limited growth with a long inter-mode at the base (appearing as stalk or pedicel) and condensed nodes present on thalamus or torus. The latter bears four types of structures— sepals, petals, stamens and carpels.
angiosperm - Structure and function | Britannica Structure and function The wide diversity in the morphological features of the plant body has been discussed above. This section will outline the underlying structural (anatomic) diversity among angiosperms. Vegetative structures
The angiosperm life cycle consists of a sporophyte phase and a gametophyte phase. The cells of a sporophyte body have a full complement of chromosomes (i.e., the cells are diploid, or 2n); the sporophyte is the typical plant body that one sees when one looks at an angiosperm. Diagram of angiosperm life cycle. Development of the male gametophyte.
Angiosperms are a type of plant belonging to the kingdom Plantae. The word Angiosperm is derived from two Greek words: angio (covered) and sperma (seed). They are the types of plants that contain flowers which is a distinct feature and the seeds are enclosed within the fruits.
Angiosperm stems are made up of seven layers as shown on the right. The amount and complexity of tissue-formation in flowering plants exceeds that of gymnosperms. In the dicotyledons, the vascular bundles of the stem are arranged such that the xylem and phloem form concentric rings.
Angiosperm eggs are fertilized and develop into a seed in an ovary that is usually in a flower. The flowers of angiosperms have male or female reproductive ...
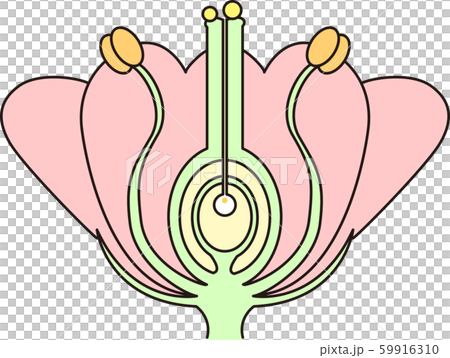
Structure and Function of Flower in Angiospermic Plants (With Diagram) The flower is a specially modified shoot responsible for sexual reproduction in angiosperms. Flowers exhibit wide variation in size, shape, colour and arrangement of floral parts. However, all flowers have the same basic plan (Fig 4.14. i)
Flower: Pedicellate, ebracteate, hermaphrodite, actinomorphic rarely zygomorphic (Iberis and Teesdalia), hypogynous, complete or incomplete (Lepidium) and tetramerous. ADVERTISEMENTS: Calyx: Sepals 4 arranged in two whorls of two each, polysepalous (2 antero-posterior and 2 lateral), 2 lateral sepals may be saccate, imbricate aestivation, inferior. Corolla: …
such as pine, spruce, and fir, in which the seeds are naked and not enclosed within fruits. The Angiospermsor flowering plantshave seeds covered by or enclosed within the fruit. The characteristic reproductive structures of the Angiosperms are the flowers. Morphologically, a flower represents a highly modified stem which bears
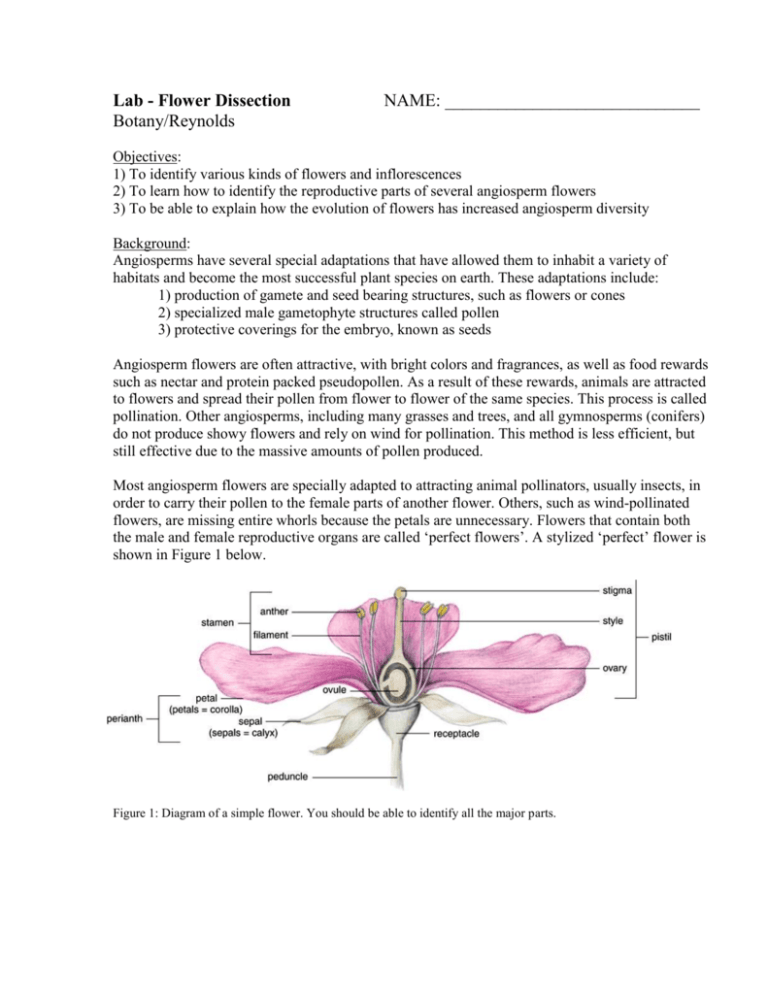
Flower diagram A COMPLETE ANGIOSPERM FLOWER FLOWER PARTS OCCUR IN WHORLS IN THE FOLLOWING ORDER- SEPALS, PETALS, STAMENS, PISTILS PEDICEL - flower stem RECEPTACLE - base of flower where other parts attach SEPALS - small and green, collectively called the CALYX PETALS - often large and showy, collectively called the COROLLA
Flowers with five parts per whorl are a synapomorphy for the Pentapetalae, a large clade that includes most eudicots (= Superrosids + Superasterids; see the diagram at the bottom of this page). Floral parts in multiples of three, typical of monocots, might be the ancestral angiosperm condition (see here ).
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, ... Diagram of flower parts. Parts ... Recently discovered angiosperm fossils such as Archaefructus, along with further discoveries of fossil gymnosperms, suggest how angiosperm characteristics may have been acquired in a series of steps. An early fossil of a flowering plant, Archaefructus liaoningensis from China, is …
General Structure of Seed (With Diagram) | Angiosperms | Botany. A typical matured seed of angiosperms consists of two parts: 1. Seed Coat 2. Kernel. 1. Seed Coat: Seed coat is the protective covering of seed, developed from integument of the ovule.









(121).jpg)


(119).jpg)













Comments
Post a Comment