40 eukaryotic cell diagram with labels
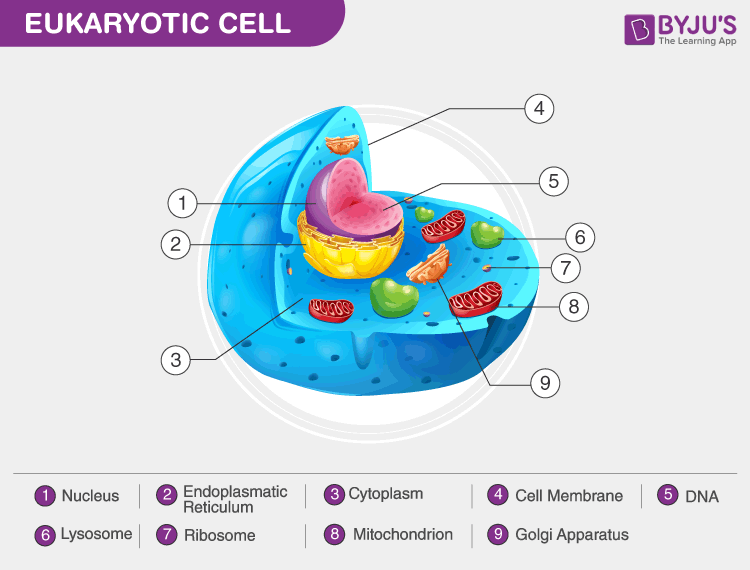
Eukaryotic Cell. Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Eukaryotic cell diagram labelling game Eukaryotic cell diagram labelling game What do microscopic amoebae, pine trees, Portobello mushrooms, and giant whales have in common in terms of their cellular structure? All of these organisms have eukaryotic cells, which mean they contain membrane-bound organelles that their prokaryotic rivals sadly lack.
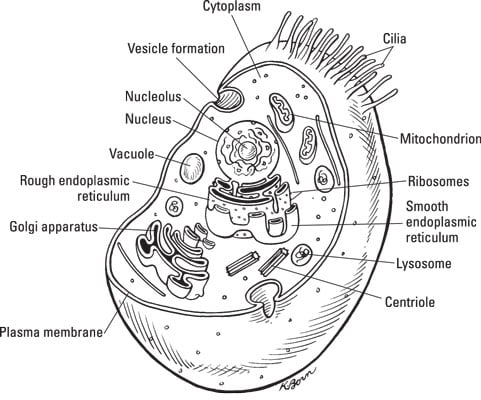
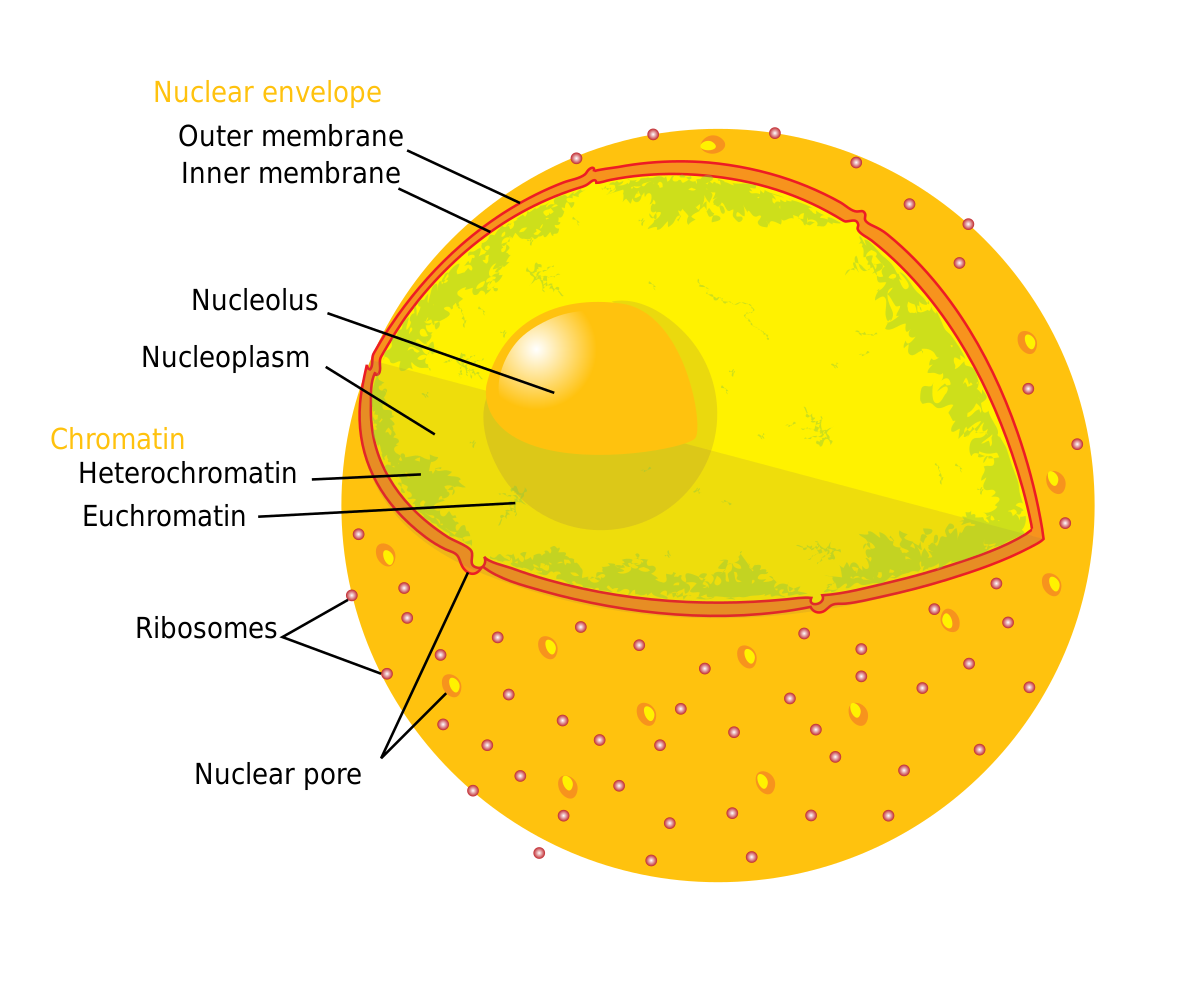
Solve the Cell Model Jigsaws. Nucleus: The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. Within each nucleus is nuclear chromatin that contains the organism's genome. The chromatin is efficiently packaged within the ...
Eukaryotic cell diagram with labels
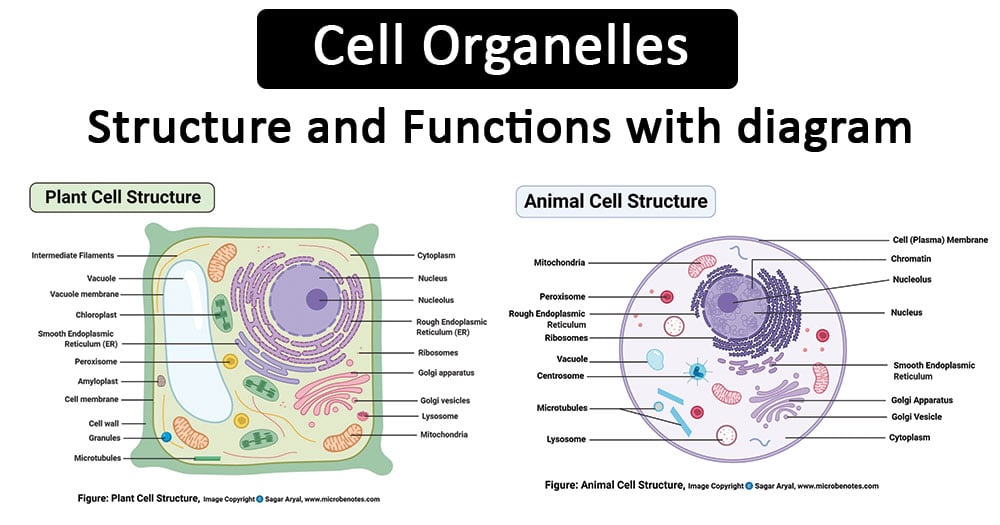
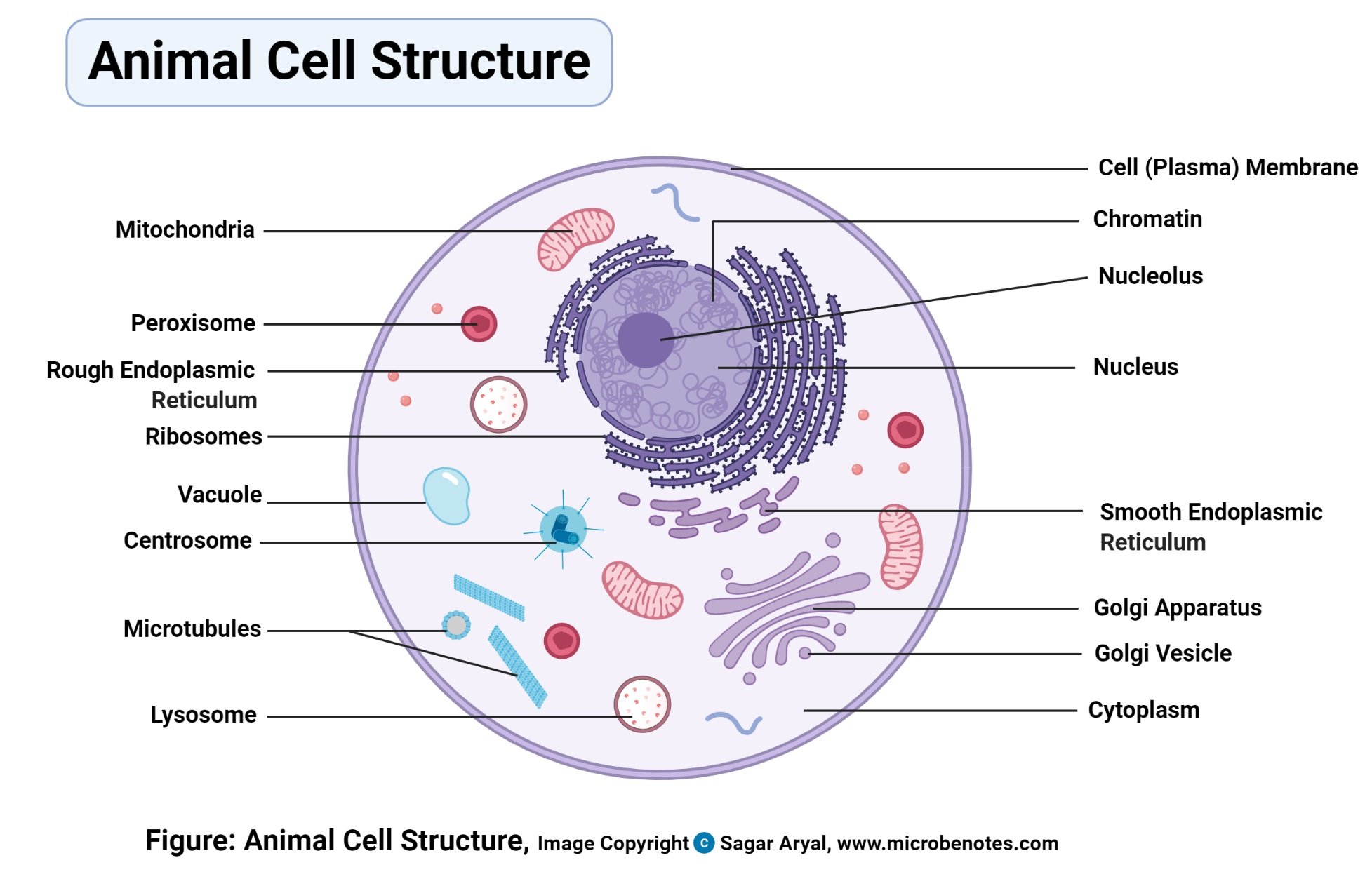
Diagram Of Animal Cell Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast. The animal cell diagram is widely asked in Class 10 and 12 examinations and is beneficial to understand the structure and functions of an animal. Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. These differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined under an electron microscope. Observe the labelled diagram of plant cell structure as given below: Animal cells are eukaryotic cells. They contain membrane-bound nuclei. Diagram of Animal Cell is beneficial in understanding the structure and functions of an animal. This article comprehends a brief explanation of the different parts of an animal cell with a well-labelled diagram. Table of Content What is Animal Cell? Diagram of Animal Cell
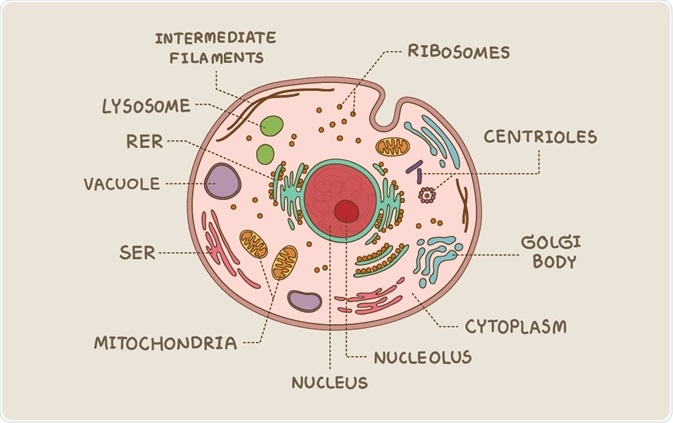
Eukaryotic cell diagram with labels. 3. FREE Printable. Prokaryotic Cell Diagram. to help you remember prokaryotes parts and pieces. Cytoskeleton: It's a relatively recent scientific discovery that rod-shaped bacteria and Archaea possess cytoskeletal proteins that function similarly to the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. This scaffolding provides structural support to the cell ... Introduction to eukaryotic cells. By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells are characterized by numerous membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others. As observed in the labeled animal cell diagram, the cell membrane forms the. This organelle has two major functions: Teks 7.12d differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, . Definition. A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum.Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals.These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells found in domains Archaea and Bacteria.
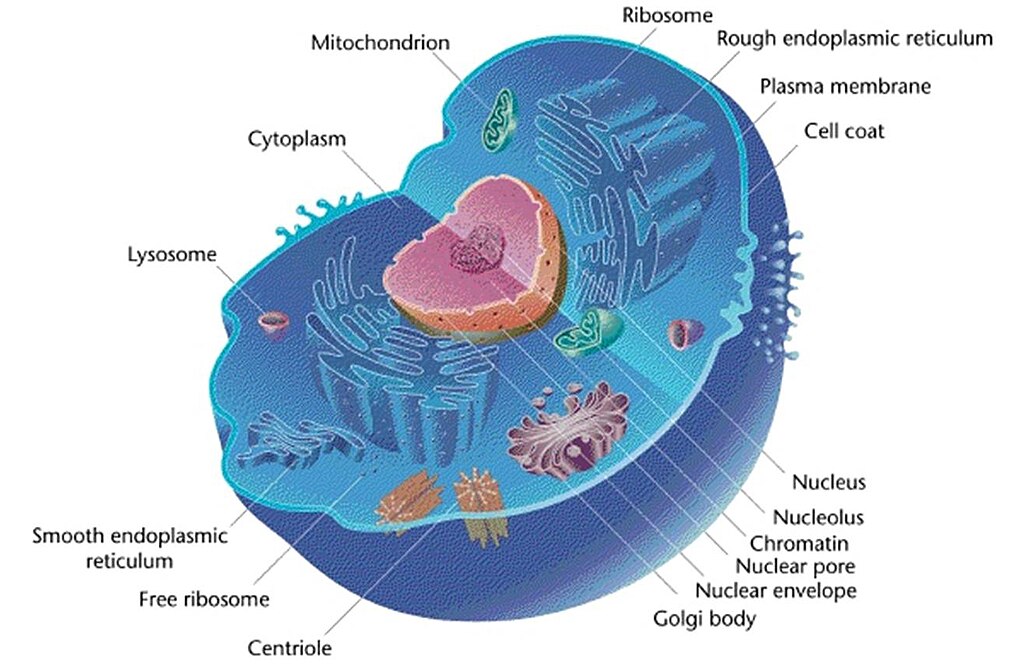
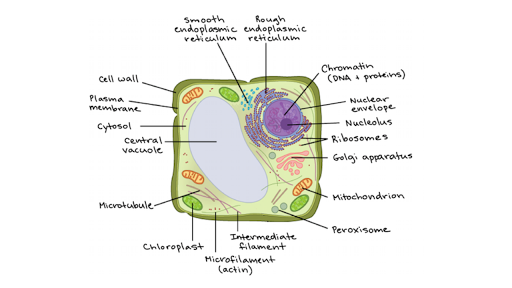
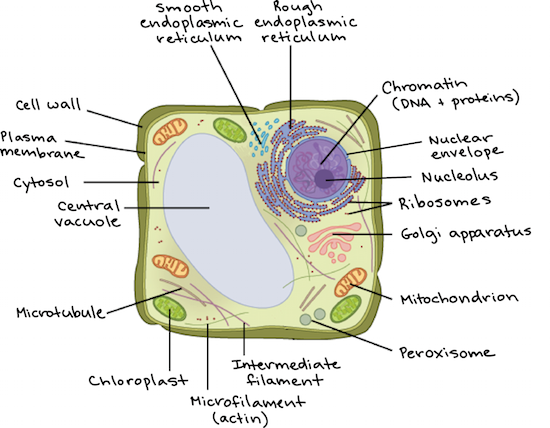
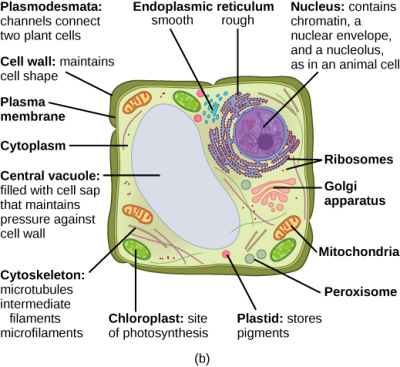
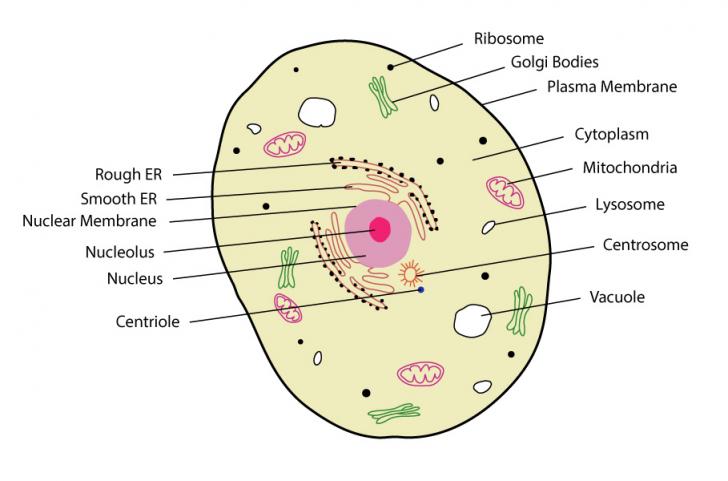
Animal Cell - Science Quiz: Animal cells are packed with amazingly specialized structures. One vital part of an animal cell is the nucleus. It's the cell's brain, employing chromosomes to instruct other parts of the cell. The mitochondria are the cell's powerplants, combining chemicals from our food with oxygen to create energy for the cell. a network of double membranes; attached to the outside of the membranes synthesize proteins that are moved into the cisternal space where carbohydrates are added to make glycoproteins. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum. a network of double membranes; no ribosomes are attached. Golgi apparatus. Eukaryotic cells 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. Figure 2.3.1 - Annotated drawing of an animal cell 2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, that are found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae which means they have a membrane-bound nucleus. They have a variety of membrane-bound cell organelles that perform various specific functions to maintain the normal functioning of the plant cell.
Eukaryotic cells include animal cells - including human cells - plant cells, fungal cells and algae. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a membrane-bound nucleus. That's distinct from prokaryotic cells, which have a nucleoid - a region that's dense with cellular DNA - but don't actually have a separate membrane-bound compartment like the nucleus. There is an interlocking three dimensional network of protein filaments throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell which is called as cytoskeleton and is visible under the electron microscope. Cytoskeleton provides structure and organisation to the cytoplasm and shape to the cell. It also helps to produce motion of organelles or of the whole cell. Eukaryotic cell diagram mentioned below depicts different cell organelles present in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, lysosomes are clearly mentioned in the diagram. Explore more about Cell organelles and eukaryotic cells 1. Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization, organelles, cell envelopes, ribosome size and component molecules, and cytoskeleton. 2. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe. 56
A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles. There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Where, prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else. From amoebae to earthworms to mushrooms, grass ...
This Schematic Diagram Shows A Generic Animal Cell And The Organelles Including The Nucleus En Animal Cells Worksheet Human Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure. Prokaryotic Cell Structure A Visual Guide Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotes.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 7. Extension Questions Read This! All cells undergo cellular respiration for the production of energy. Energy is necessary for all metabolic activity within the cell. The formula for cellular respiration is C. 6. H. 12. O. 6 + 6O. 2 ⎯⎯→ 6CO. 2 + 6H. 2. O + energy/ATP Plants carry out photosynthesis for the production of glucose.
Labelled Diagram Of A Human Cell Bone Cell Labeled Diagram Animal Cell Free Printable To Label Animal Cell Eukaryotic Cell Cell
Prokaryotic cell to label - Labelled diagram. nucleoid region, pili, ribosomes, flagellum, plasmid, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, cell wall, capsule.
Labels can be used once or more than once. Can you identify the cellular structures and their functions in this diagram of a eukaryotic cell. Above all eukaryotic cells are defined by the presence of a nucleus surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane. Lysosome found in animal cells but not most plant cells.
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move. nucleoid. A non-membrane-bounded region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is concentrated. cytoplasm. A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended.
Cell Organelles Definition. Cell organelles are specialized entities present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function. There are various cell organelles, out of which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. However, some organelles are specific to one particular type of cell ...
Although there are differences among eukaryotes (creature that range from amoebae to elephant), overall, eukaryotic cells share many characteristics. Here's a breakdown. Article Summary: Animals, plants, fungi, protists, algae, and water & slime molds are eukaryotes, organisms composed of one or more nucleated cells.
What is Label The Cell Structures In The Diagram. An embryonic cell divides again and again. 3:- Identify structures from 2. Cell structures and their functions can be described in many ways, but cells and their components can be assumed to have three distinct functions: Serving as a physical boundary or In fact, some living things consist of only a single cell.
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells. They contain membrane-bound nuclei. Diagram of Animal Cell is beneficial in understanding the structure and functions of an animal. This article comprehends a brief explanation of the different parts of an animal cell with a well-labelled diagram. Table of Content What is Animal Cell? Diagram of Animal Cell
Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. These differences can be clearly understood when the cells are examined under an electron microscope. Observe the labelled diagram of plant cell structure as given below:
Diagram Of Animal Cell Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in that they do contain cell walls and chloroplast. The animal cell diagram is widely asked in Class 10 and 12 examinations and is beneficial to understand the structure and functions of an animal.











/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)
/Prokaryotic-and-Eukaryotic-cells-58f679525f9b581d593bbaed.jpg)












Comments
Post a Comment