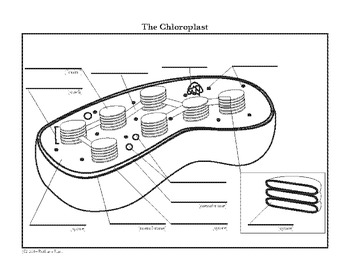
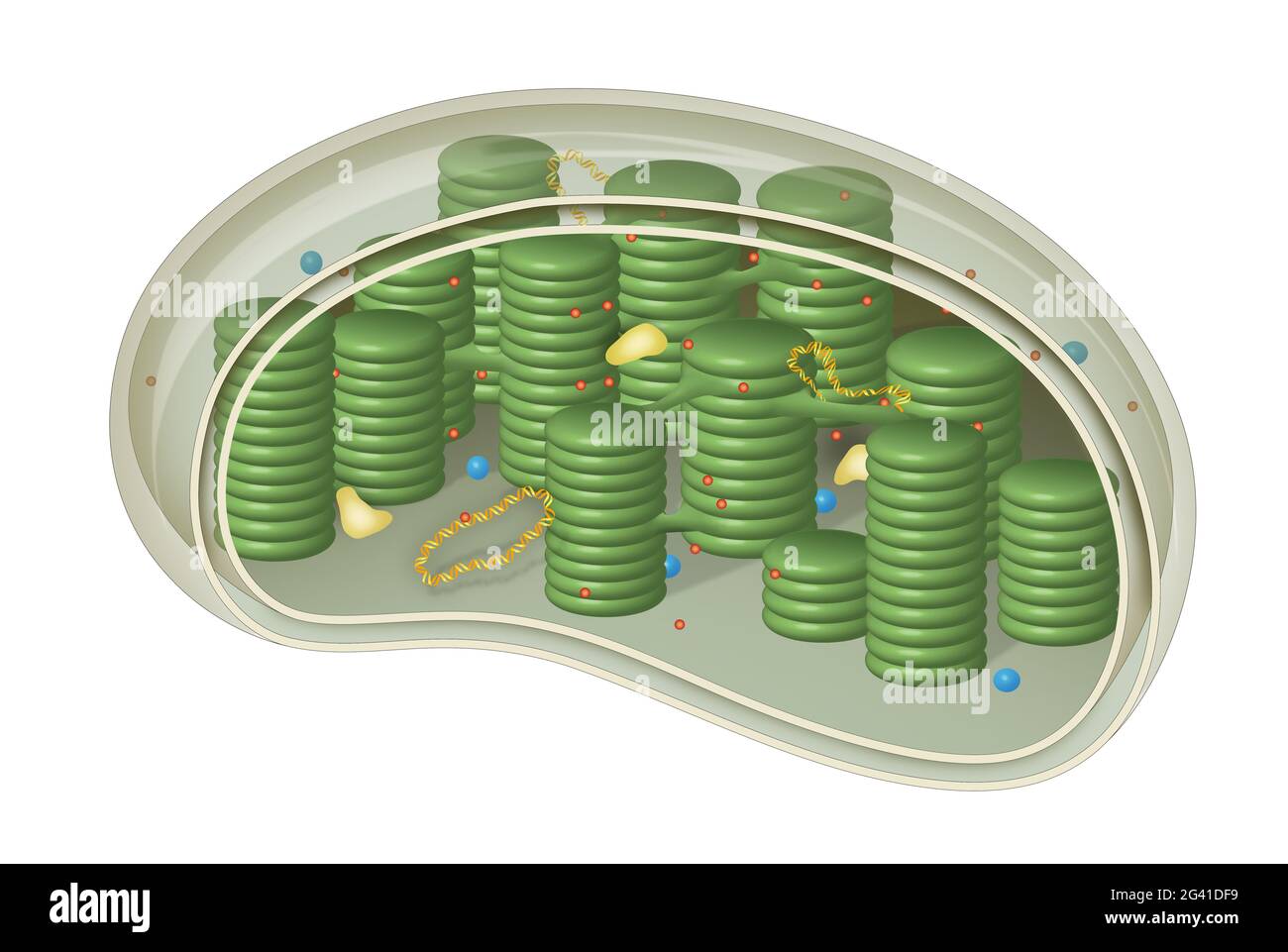
42 diagram of a chloroplast
Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. Proplastids are immature, undifferentiated cells that develop into different types of plastids. A proplastid that develops into a chloroplast only does so... Bio Factsheet Chloroplasts - Structure and Function Number 198... Chloroplasts - Structure and Function Isolating chloroplasts In green plants most of the chloroplasts are found in The diagram shows the arrangement of photosytems in the thylakoid membrane, and summarises the processes that take place there. light H+ light NADP...
What is the biological function of chloroplast? - Rs' Science What is chloroplast? The structure of chloroplasts. Chloroplasts convert the light energy of the Sun into sugars (a process called photosynthesis) that can be used by cells. [In this figure] Cartoon diagram showing the chloroplast division steps.

Diagram of a chloroplast
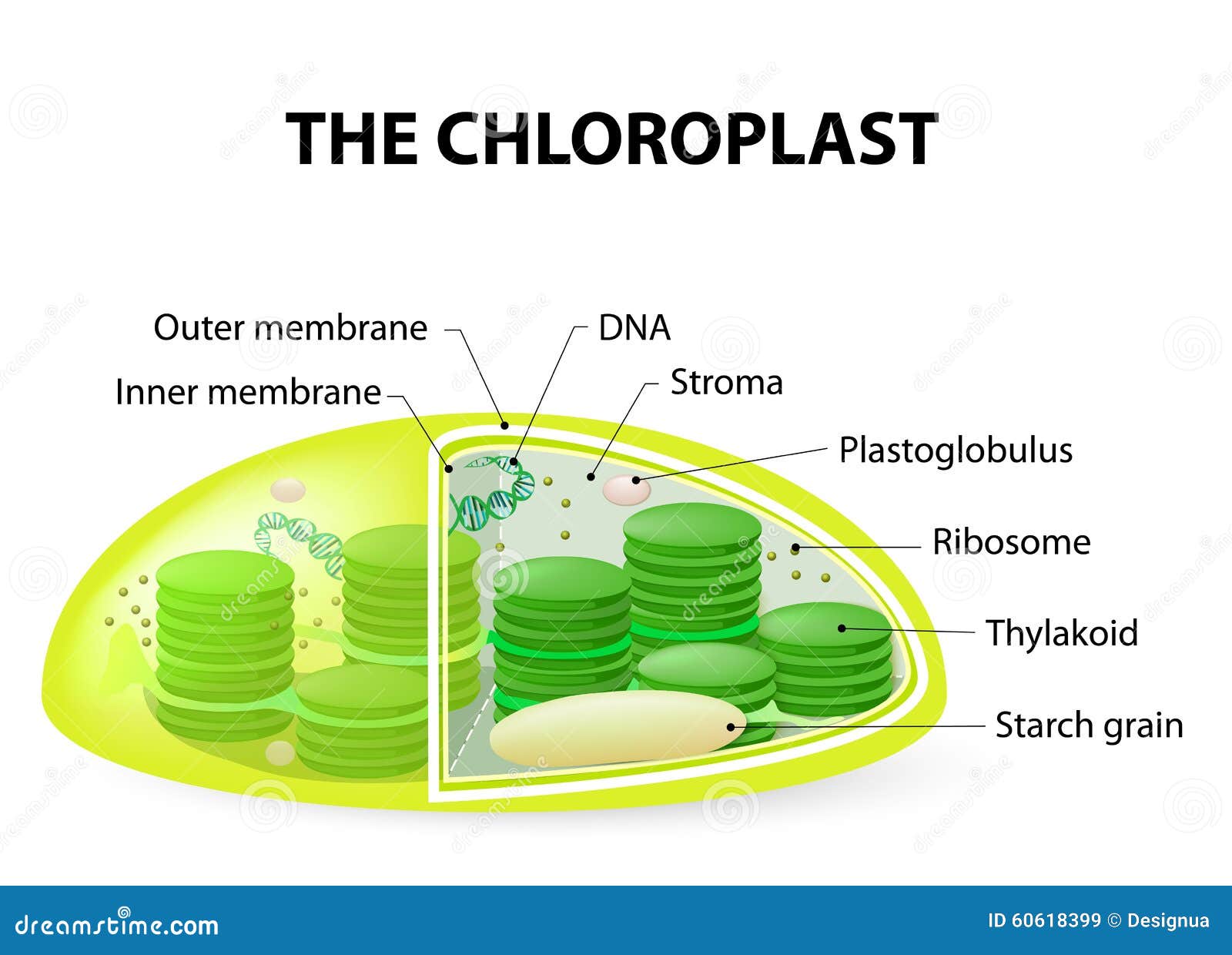
Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic... Basic process of chloroplast genetic engineering, diversity in intergenic spacer regions, and impact of transgene integration (endogenous versus heterologous genome The schematic diagram represents recombination between the tobacco transplastomic genome and the lettuce transformation vector [128]. Chloroplast - Definition, Structure, Functions with Diagram The chloroplast is a type of cell organelle called plastids found in plants and blue-green algae. It contains the pigment chlorophyll that traps the light energy of the sun to convert them to the chemical energy of food by Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbenotes.com. Functions of Chloroplast Functions of Chloroplast. Absorption of light energy and conversion of it into biological energy. Production of NAPDH2 and evolution of oxygen through the Chloroplasts, like the mitochondria use the potential energy of the H+ ions or the hydrogen ion gradient to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Diagram of a chloroplast. chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram Chloroplast, structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are a type of plastid that are distinguished by their green color, the result of specialized chlorophyll pigments. Native architecture of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast revealed by in... (A) Cross-section diagram of a Chlamydomonas cell. The chloroplast is shown in color. Much of our understanding of chloroplast architecture comes from conventional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) studies (Hodge et al., 1955; Sager and Palade, 1957; Heslop-Harrison, 1963... Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram Figure: Diagram of Chloroplasts. Structure of Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts found in higher plants are generally biconvex or planoconvex shaped. In different plants, however, chloroplasts may have different shapes, varying from spheroid, filamentous saucer-shaped, discoid or ovoid-shaped. Wikizero - Chloroplast Diagram of a four membraned chloroplast containing a nucleomorph. The genes in the phagocytosed eukaryote's nucleus are often transferred to the secondary host's nucleus.[18] Cryptomonads and chlorarachniophytes retain the phagocytosed eukaryote's nucleus, an object called a nucleomorph...
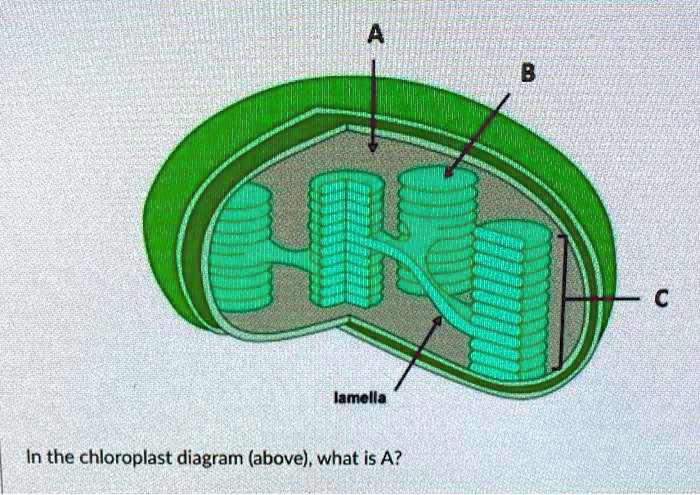
› watchPhotosynthesis | Photosynthesis in plants | Photosynthesis ... Photosynthesis | Photosynthesis in plants | Photosynthesis - Biology basics for children | Science | elearninPhotosynthesis Hello Kids .... Do you know how p... › science › plant-cellplant cell | Definition, Characteristics, & Facts | Britannica A chloroplast is a type of plastid (a saclike organelle with a double membrane) that serves as the site of photosynthesis, the process by which energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for growth. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll to absorb light energy. Chloroplast | BioNinja | Click on the diagram to show / hide labels • Annotation of a diagram to indicate the adaptations of a chloroplast to its function. Electron micrographs of a chloroplast may differ in appearance depending on where the cross-section occurs. Typically, chloroplast diagrams should display the following features: Usually round in appearance... › scitable › topicpagePhotosynthesis, Chloroplast | Learn Science at Scitable Figure 4: Diagram of a chloroplast inside a cell, showing thylakoid stacks Shown here is a chloroplast inside a cell, with the outer membrane (OE) and inner membrane (IE) labeled.
Chloroplast Transformation in Plants (With Diagram) Chloroplast Transformation in Plants! The chloroplasts (plastids) and mitochondria are believed to have evolved from prokaryotes during the course of Further, many of the proteins that function in chloroplasts and mitochondria are encoded by nuclear genes- and then transported to the organelle. File:Chloroplast diagram.svg - Wikimedia Commons File:Chloroplast diagram.svg. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Jump to navigation Jump to search. DescriptionChloroplast diagram.svg. A vectorised version of File:Chloroplast-new.jpg. A diagram showing the simple structure of a chloroplast. Chloroplasts | CIE A Level Biology Revision Notes FREE & DOWNLOADABLE Biology revision notes on Chloroplasts. Designed by Save My Exams teachers for the CIE A Level Biology (9700) syllabus. Make sure you can identify the structures of a chloroplast on a diagram AND that you can explain the function of each of these structures. Diagram Of Chloroplast || How To Draw Chloroplast... - YouTube Enrich Minds is a project that we have initiated keeping in mind both academics as well as art. Our motto is to create quality content that will help our users enhance both, logical as well as the creative capabilities of our brain.
Chloroplast - Wikipedia A chloroplast /ˈklɔːrəˌplæst, -plɑːst/ is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it...
Chloroplast - New World Encyclopedia Chloroplasts are organelles (compartments) found in plant cells and eukaryotic algae that conduct photosynthesis. Utilizing chlorophyll and water, chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun to produce the free energy stored in ATP and NADPH through a process called photosynthesis.
chloroplast Anticlockwise from top left: Plant cell containing chloroplasts (green); diagram of chloroplast; micrograph of chloroplast. Fig 2. A single chloroplast (A), typical of those found in the palisade layer of cells (B) of a land plant, is contained in a membrane (1). Its interval structure comprises a series of...
6 Recovery of intact chloroplasts through Percoll | ScienceDirect Topics Chloroplasts and Chloroplast Genomes. Chloroplasts are chlorophyll-containing organelles in plant cells; they play a vital role for life on Earth since The existence of functioning DNA in chloroplasts (chloroplast DNA (cpDNA)) and other plastids is one of the main findings supporting their origin as...
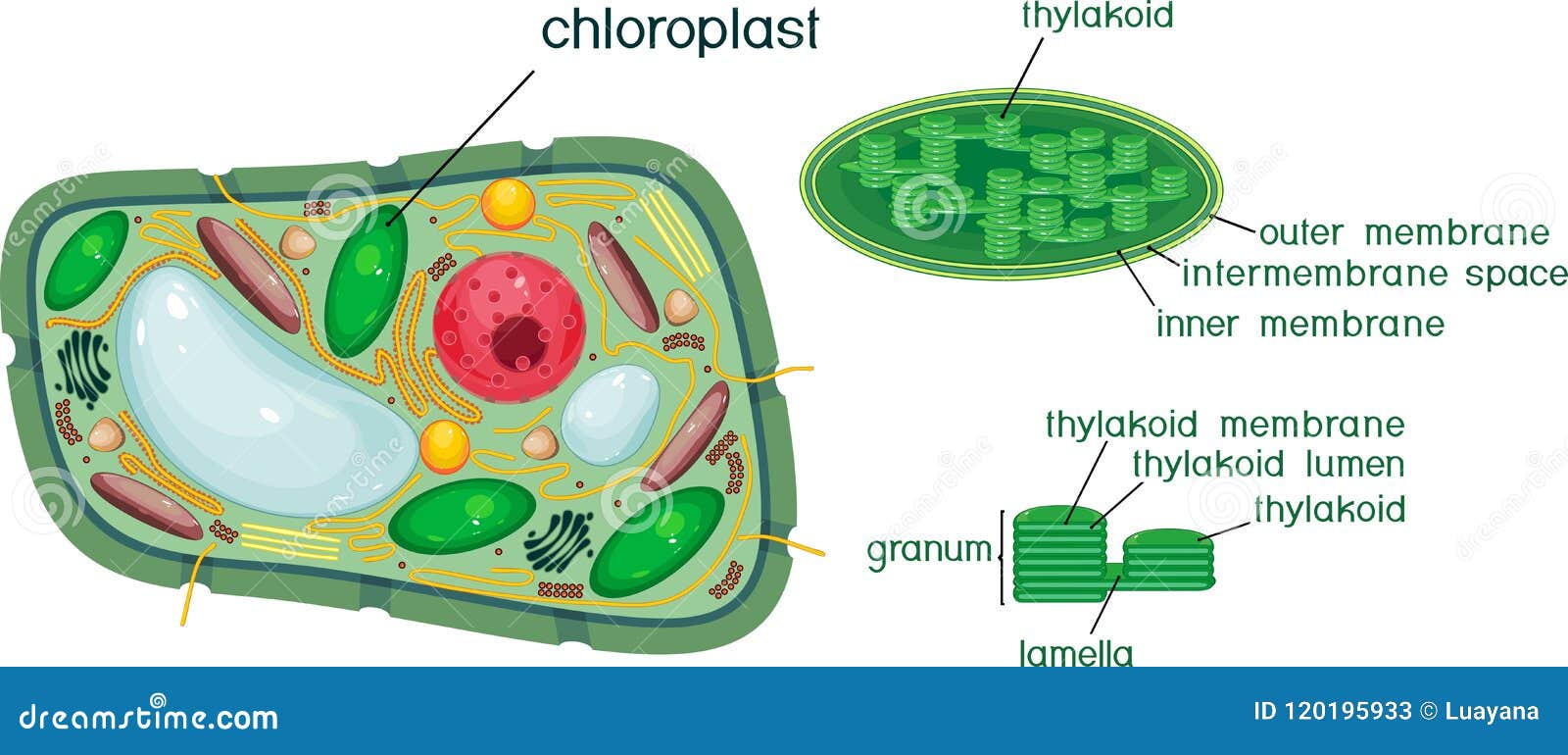
› wp-content › uploadsPlant Cells - Definition, Diagram, Structure & Function Plant Cells - Definition, Diagram, Structure & Function The cell is the basic unit of life in all organisms. Like humans and animals, plants are also composed of several cells. The plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall which is involved in providing shape to the plant cell. Apart from the cell wall, there are other organelles that are
Chloroplasts Chloroplasts. The sketch of the chloroplast above was made from an electron micrograph of a chloroplast from a higher order plant (Levy). Plants use energy from the sun in tiny energy factories called chloroplasts. Using chlorophyll in the process called photosynthesis, they convert the sun's...
Diagram of a chloroplast Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Diagram of a chloroplast. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. The fluid of the chloroplast surrounding the thylakoid membrane; involved in the synthesis of organic molecules from carbon dioxide and water.
Chloroplast - CreationWiki, the encyclopedia of creation science Chloroplast is an organelle in plant cells, algae, and some protists that performs photosynthesis. The purpose for having chloroplast in plants is to produce food: glucose and other sugars. The chloroplast has chlorophyll (a green pigment), which is responsible for giving plants their characteristic color.
› plant-cellPlant Cell – Structure, Parts, Functions, Types, and Diagram Oct 21, 2021 · Plant Cell Diagram 1) Cell Wall. It is the outermost, protective layer of a plant cell having a thickness of 20-80 nm. Cell walls are made up of carbohydrates such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin and a complex organic polymer called lignin.
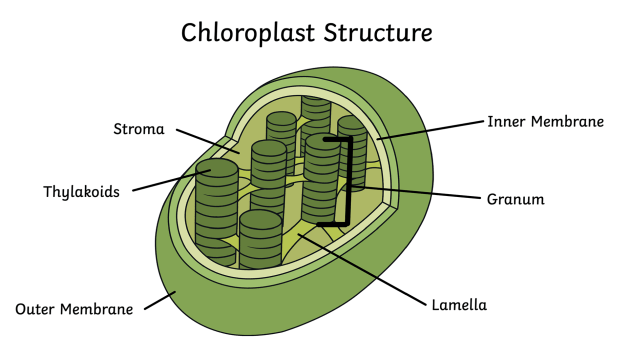
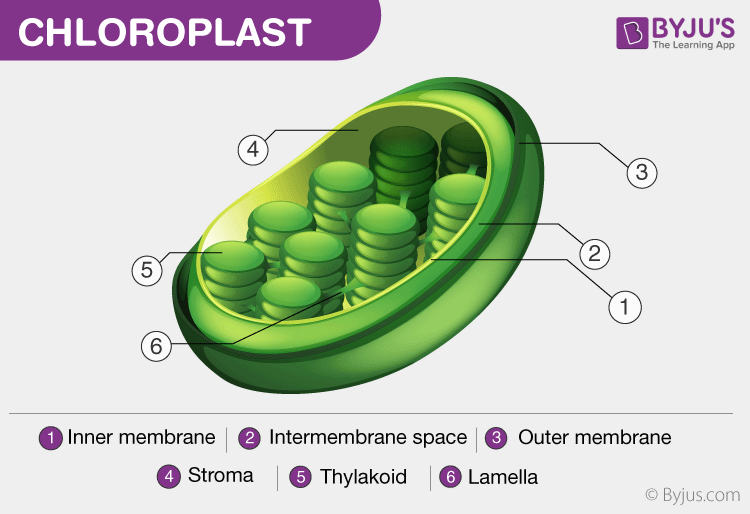
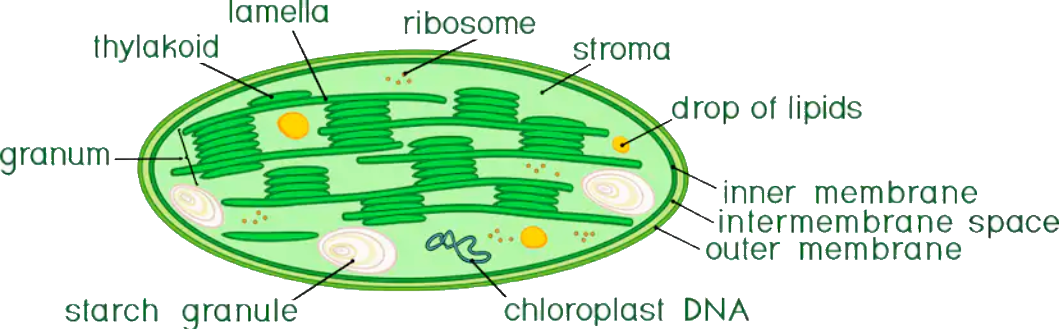
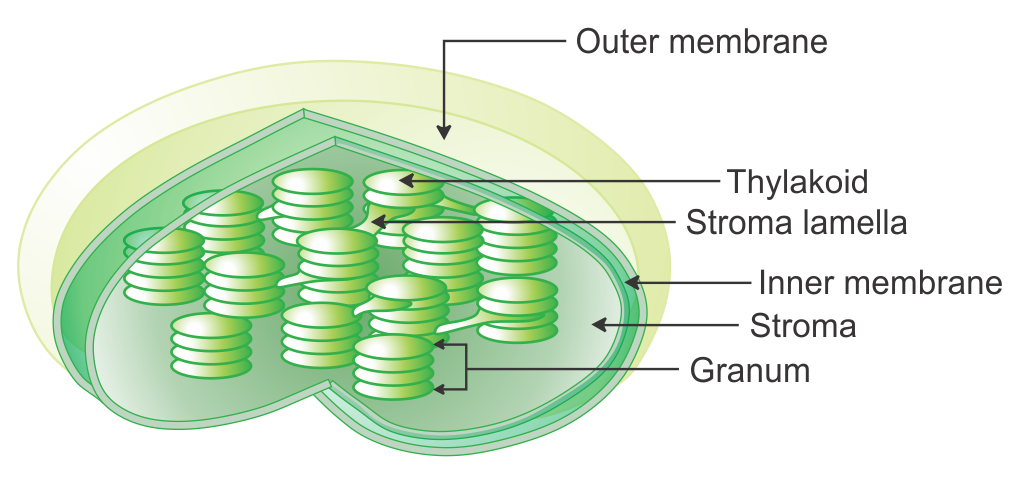
Chloroplast Diagram - Pictures, Photos & Images of Plants - Science... Photo name: Chloroplast Diagram Picture category: Plants Image size: 63 KB Dimensions: 700 x 495 Photo description: This diagram shows the basic structure of a chloroplast, featuring an inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane, stroma (aqueous fluid), lamella, lumen and more.
Difference Between Chloroplast and Mitochondria | Structure... What is the difference between Chloroplast and Mitochondria? Chloroplasts are found in plant and The major function of chloroplast is the production of organic molecules, glucose from CO2 and A diagram of electron transport chain is shown in figure 6. The produced ATPs pass through the...
Chloroplast - RationalWiki Chloroplasts are the specialised organelles found in almost all plant species and are the means by which photosynthesis occurs. All of the green structures in plants, including stems and unripened fruit, contain chloroplasts, but the majority of photosynthesis activity in most plants occurs in the leaves.
byjus.com › biology › chloroplastsChloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out.
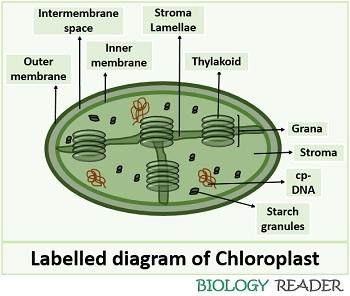
Explain the structure of the chloroplast. Draw a neat labelled diagram. The heterogeneous nature of chloroplast is due to the presence of disc-like structures i.e., grana, in a colourless matrix called stroma. Draw a labelled diagram showing the fine structure of a chloroplast a simple equation for the overall process of photosynthesis.
Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary This diagram shows the parts of a chloroplast. Evolution of Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts have their own, separate DNA that is circular, like that of a bacterial cell, and inherited maternally (only from the mother plant alga).
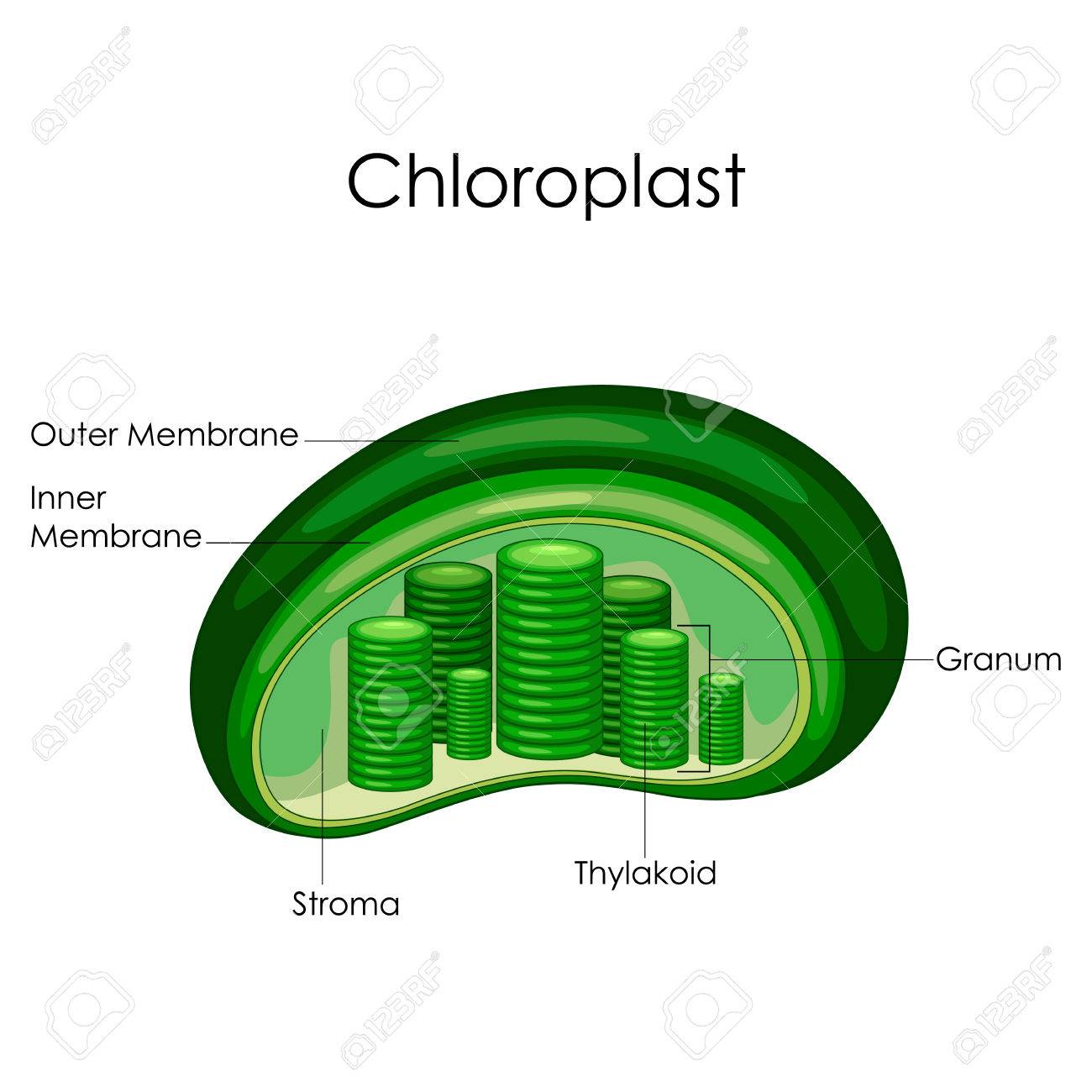
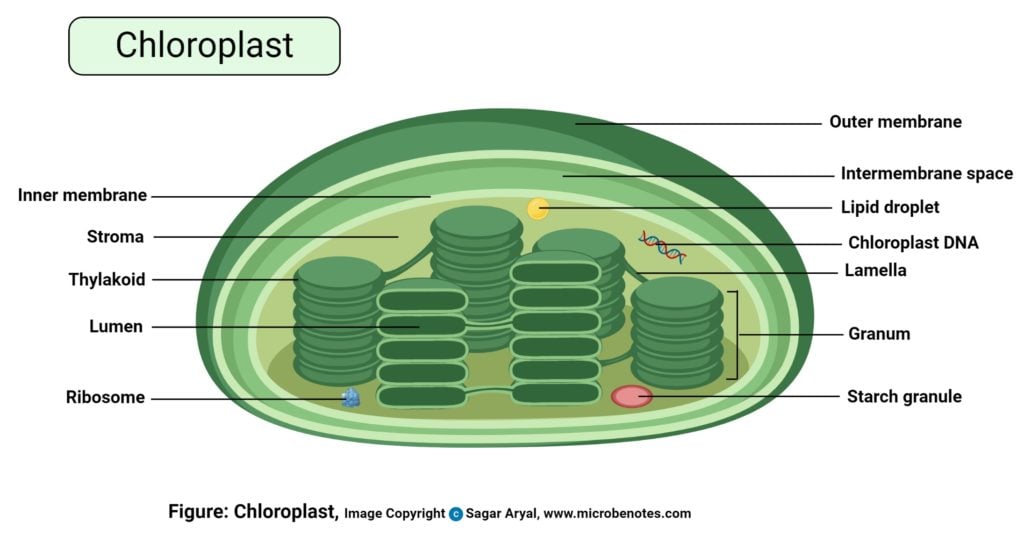
microbenotes.com › cell-organellesCell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Labeled ... Nov 28, 2021 · Chloroplast. A chloroplast is a type of plastic that is involved in photosynthesis in plants and algae. Chloroplast contains an essential pigment called chlorophyll necessary to trap sunlight for the production of glucose. Structure of Chloroplast. It is a double-membraned structure with its own DNA which is inherited from the previous chloroplast.
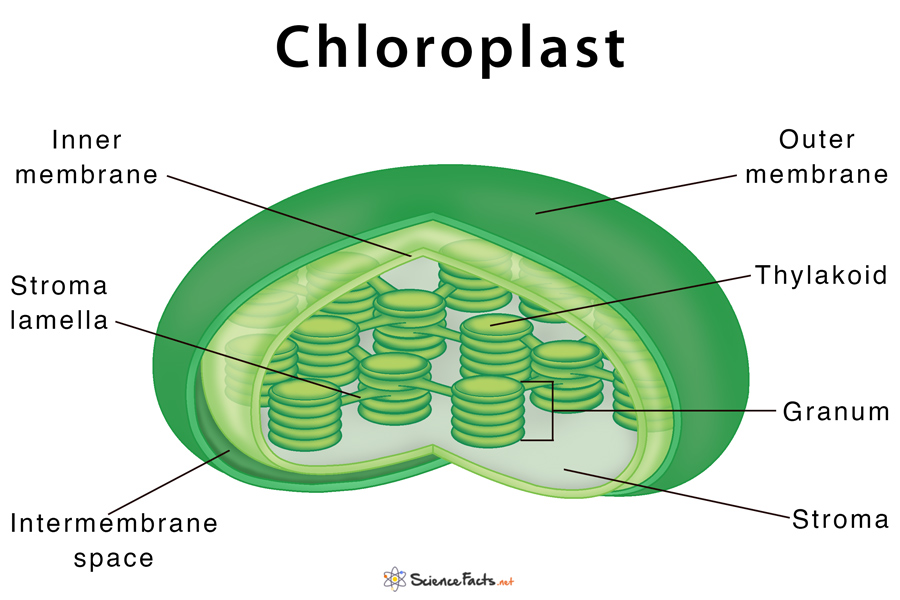
Above: Diagram of the structure of a chloroplast The following diagram of a chloroplast shows the structure of a chloroplast including the main parts - the chloroplast envelope, the stroma The model shown above indicates the relative sizes of the structures within a chloroplast and how individual chloroplasts can include up to about 50 thylakoids.
Chloroplast: Definition, Structure & Function (with Diagram) | Sciencing Chloroplasts in plants and algae produce food and absorb carbon dioxide through the photosynthesis process that creates carbohydrates, such as sugars and starch. The active components of the chloroplast are the thylakoids, which contain chlorophyll, and the stroma, where carbon fixation takes...
Structure of Chloroplasts Essentially, chloroplasts are plastids found in cells of higher plants and algae as sites of photosynthesis. This makes them the most important cell organelles as plants are the primary producers and the base of all food chains.
Functions of Chloroplast Functions of Chloroplast. Absorption of light energy and conversion of it into biological energy. Production of NAPDH2 and evolution of oxygen through the Chloroplasts, like the mitochondria use the potential energy of the H+ ions or the hydrogen ion gradient to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Chloroplast - Definition, Structure, Functions with Diagram The chloroplast is a type of cell organelle called plastids found in plants and blue-green algae. It contains the pigment chlorophyll that traps the light energy of the sun to convert them to the chemical energy of food by Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbenotes.com.
Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic... Basic process of chloroplast genetic engineering, diversity in intergenic spacer regions, and impact of transgene integration (endogenous versus heterologous genome The schematic diagram represents recombination between the tobacco transplastomic genome and the lettuce transformation vector [128].
























Comments
Post a Comment